Owning a 2012 MK6 Jetta GLI means enjoying a balance of performance and practicality. However, like any vehicle, it can encounter hiccups. One such hiccup is the dreaded “Check Engine” light illuminating your dashboard, often accompanied by the cryptic VCDS fault code 01335. This code can be a head-scratcher, leaving you wondering about its meaning and potential solutions. Fear not, this article aims to demystify the 01335 fault code, providing you with the knowledge to address this issue effectively.
Deciphering the 01335 Code: What Does it Mean?
In simple terms, the VCDS 01335 fault code signals a problem with your oxygen (O2) sensor. Specifically, it points to an issue with the O2 sensor downstream of the catalytic converter on Bank 1, Sensor 2.
 Oxygen Sensor Location
Oxygen Sensor Location
But what does that actually mean? Let’s break it down further:
- Oxygen Sensor: Your car’s O2 sensors are vital components of the emission control system. They measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gases to ensure optimal combustion and minimize harmful emissions.
- Bank 1: Most four-cylinder engines, like the one in your Jetta GLI, have a single bank of cylinders. So, “Bank 1” refers to the side of the engine where all cylinders are located.
- Sensor 2 (Downstream): This indicates the O2 sensor positioned after the catalytic converter. Its primary role is to monitor the converter’s efficiency.
Therefore, the 01335 code essentially tells us that the downstream O2 sensor on your 2012 Jetta GLI is not providing the expected readings, suggesting a potential issue with the sensor itself or the wiring and connections related to it.
Common Causes of the 01335 Fault Code
The 01335 fault code can arise from several common culprits. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting:
- Faulty O2 Sensor: The most likely culprit is a malfunctioning downstream O2 sensor. Over time, these sensors can wear out, become contaminated, or fail completely, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Wiring or Connection Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring or connections in the O2 sensor circuit can disrupt the signal transmission, triggering the fault code.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, particularly before the downstream O2 sensor, can introduce fresh air, skewing the sensor readings.
- Catalytic Converter Issues: While less common, a malfunctioning catalytic converter can also lead to abnormal readings from the downstream O2 sensor.
 Faulty Oxygen Sensor
Faulty Oxygen Sensor
Addressing the 01335 Fault Code: A Step-by-Step Guide
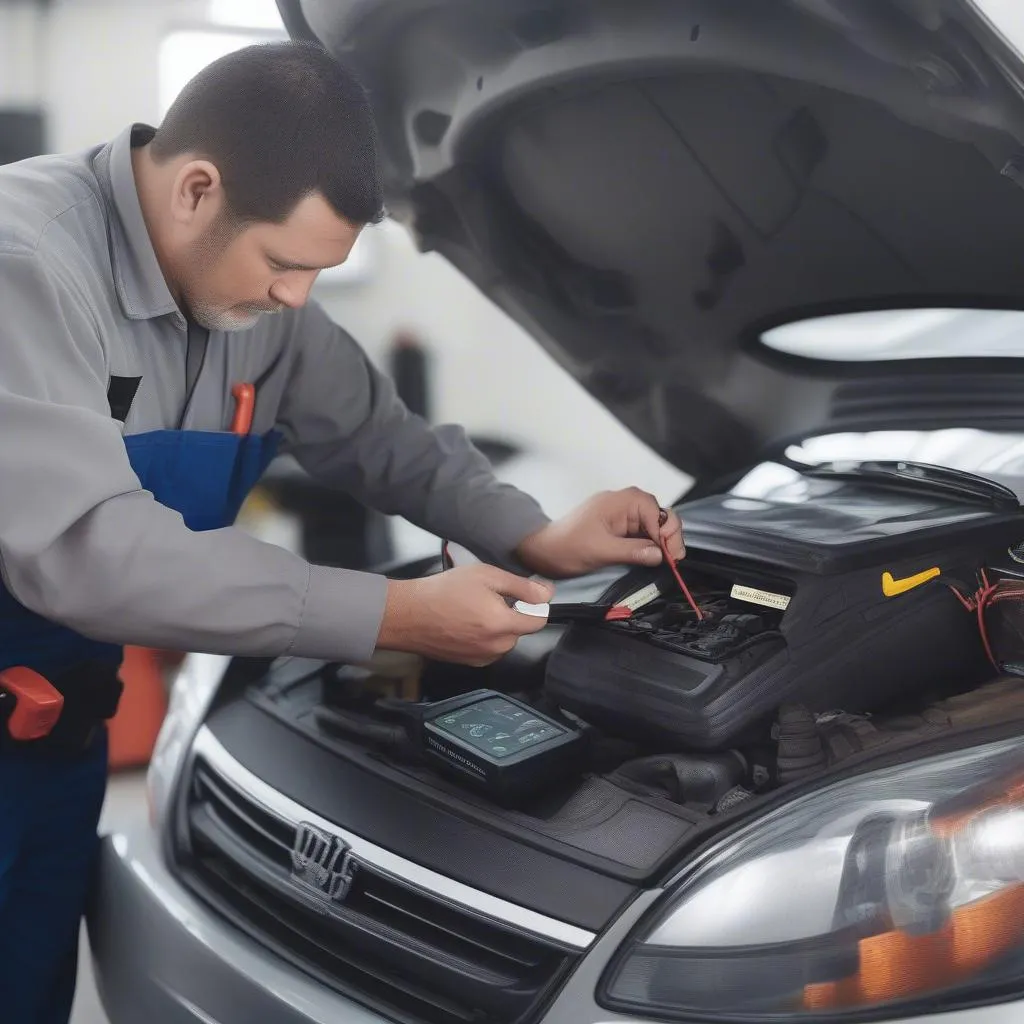 Car Diagnostic Tool
Car Diagnostic Tool
Resolving the 01335 fault code involves a systematic approach to pinpoint and rectify the underlying issue:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the wiring and connectors associated with the downstream O2 sensor. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Diagnostic Scan: Employ a reliable OBD-II scanner, like the ones offered by CARDIAGTECH, to read and clear the fault codes. This step confirms the presence of the 01335 code and ensures no other related codes require attention.
- Live Data Monitoring: Utilize the OBD-II scanner to monitor the live data stream from the downstream O2 sensor. Compare its readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if it is functioning within the expected range.
- Sensor Testing: If the sensor’s readings are out of spec, you can further test its functionality using a multimeter. Consult a reliable repair manual or seek guidance from a qualified mechanic to perform this step accurately.
- Component Replacement: Based on your diagnosis, replace the faulty component, whether it’s the O2 sensor itself, a wiring harness, or, in rare cases, the catalytic converter. Always use high-quality replacement parts that meet the manufacturer’s specifications.
Note: If you are uncomfortable working with automotive electrical systems or lack the necessary tools and expertise, it’s best to entrust the diagnosis and repair to a qualified mechanic.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Can I continue driving with the 01335 fault code?
A: While the 01335 code might not immediately render your car undrivable, it’s crucial to address it promptly. Ignoring it can lead to decreased fuel efficiency, potential damage to other engine components, and even failure to pass emissions tests.
Q: Is it safe to clear the code without fixing the issue?
A: Simply clearing the code without addressing the root cause is like silencing an alarm without addressing the fire. The code will likely reappear, and you’ll miss the opportunity to prevent potential further damage.
Q: How much does it cost to fix the 01335 fault code?
A: The repair cost can vary significantly depending on the underlying cause and labor rates in your area. Replacing an O2 sensor can range from $100 to $300, while a catalytic converter replacement can cost upwards of $1000.