In today’s world, owning a car comes with inherent risks, with theft being a major concern. An anti-theft security system is your vehicle’s first line of defense against potential thieves. But what exactly constitutes this system, and how does it provide that crucial protection for your car?
Understanding Anti-theft Systems: More Than Just an Alarm
Gone are the days when car security was synonymous with a simple alarm system. Modern anti-theft systems are complex networks of electronic components designed to deter theft and unauthorized access.
How to Identify if Your Car Has an Anti-theft System
Most modern cars come equipped with factory-installed anti-theft systems. However, if you’re unsure about your vehicle, there are telltale signs to look for:
- Visible Deterrents: Look for flashing LEDs on the dashboard or near the steering column. These often indicate an active alarm system.
- Key Fobs with Immobilizers: Modern car keys often have embedded transponders. When you attempt to start the car, the system verifies the transponder’s signal, disabling the ignition if it’s not recognized.
- Audible and Visual Alarms: A loud siren is the most recognizable feature. Some systems also include flashing headlights or honking horns.
Common Components of an Anti-theft System
To understand how these systems work, let’s break down their key components:
- Engine Immobilizer: This system prevents the engine from starting without the presence of the correct key or transponder signal.
- Car Alarm System: Triggered by unauthorized entry attempts, the alarm uses sensors to detect forced entry, glass breakage, or vehicle movement.
- Tracking System: Some advanced systems use GPS or cellular technology to track the vehicle’s location in case of theft. This can be invaluable for recovery.
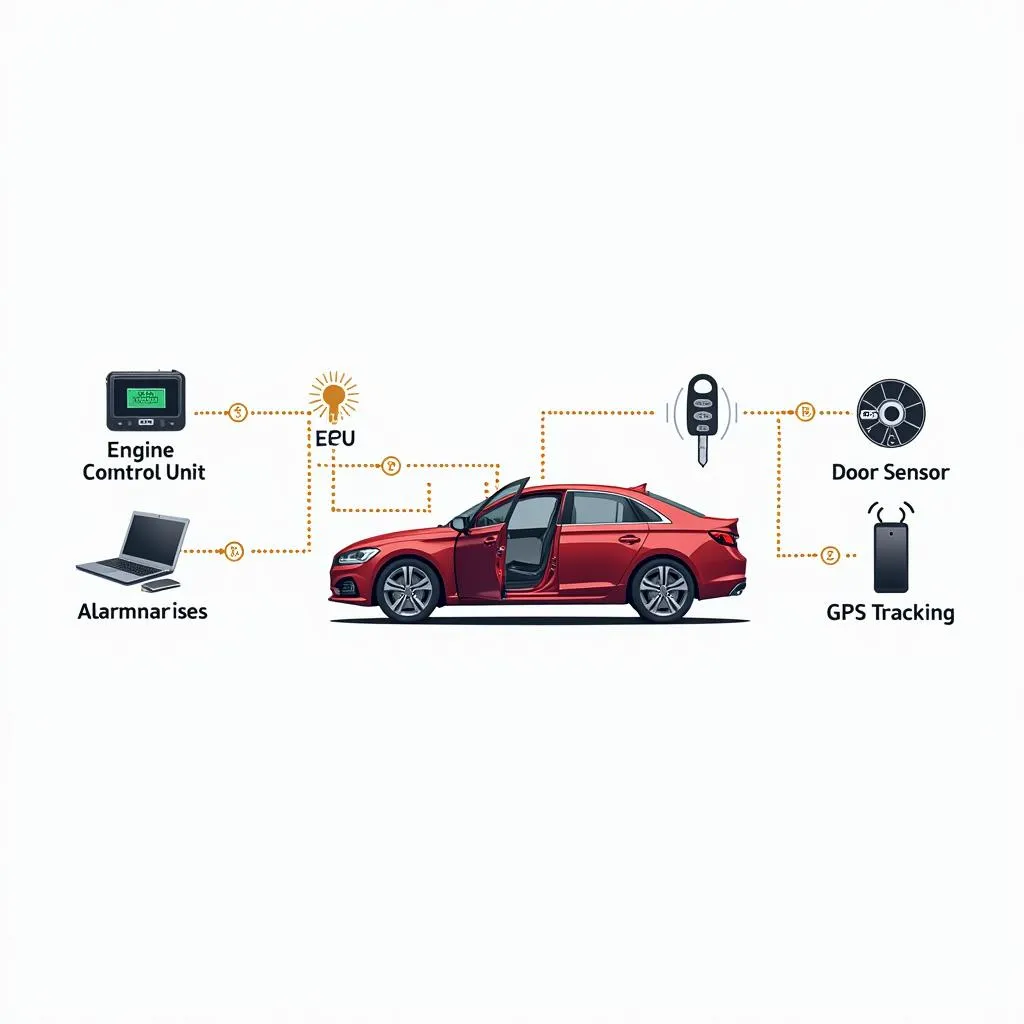 Car anti-theft system components diagram
Car anti-theft system components diagram
Diagnosing Problems with Your Anti-theft System
Malfunctions within your anti-theft system can be frustrating. Here’s what you need to know:
Recognizing the Signs of a Problem
Several indicators might point to a fault within your anti-theft system:
- Engine Cranks but Won’t Start: This is a common symptom of an immobilizer issue. The system might not be recognizing your key’s transponder.
- Rapid Flashing Dashboard Lights: Especially around the ignition area, rapid flashing can indicate an attempted breach or system malfunction.
- Alarm Randomly Activates: A malfunctioning sensor might be triggering false alarms.
Equipment Needed for Diagnostics
Before attempting any repairs, it’s crucial to diagnose the issue accurately:
- OBD-II Scanner: This tool connects to your vehicle’s computer system, allowing you to read diagnostic trouble codes related to the anti-theft system.
- Digital Multimeter: Useful for testing electrical circuits and components like sensors and wiring.
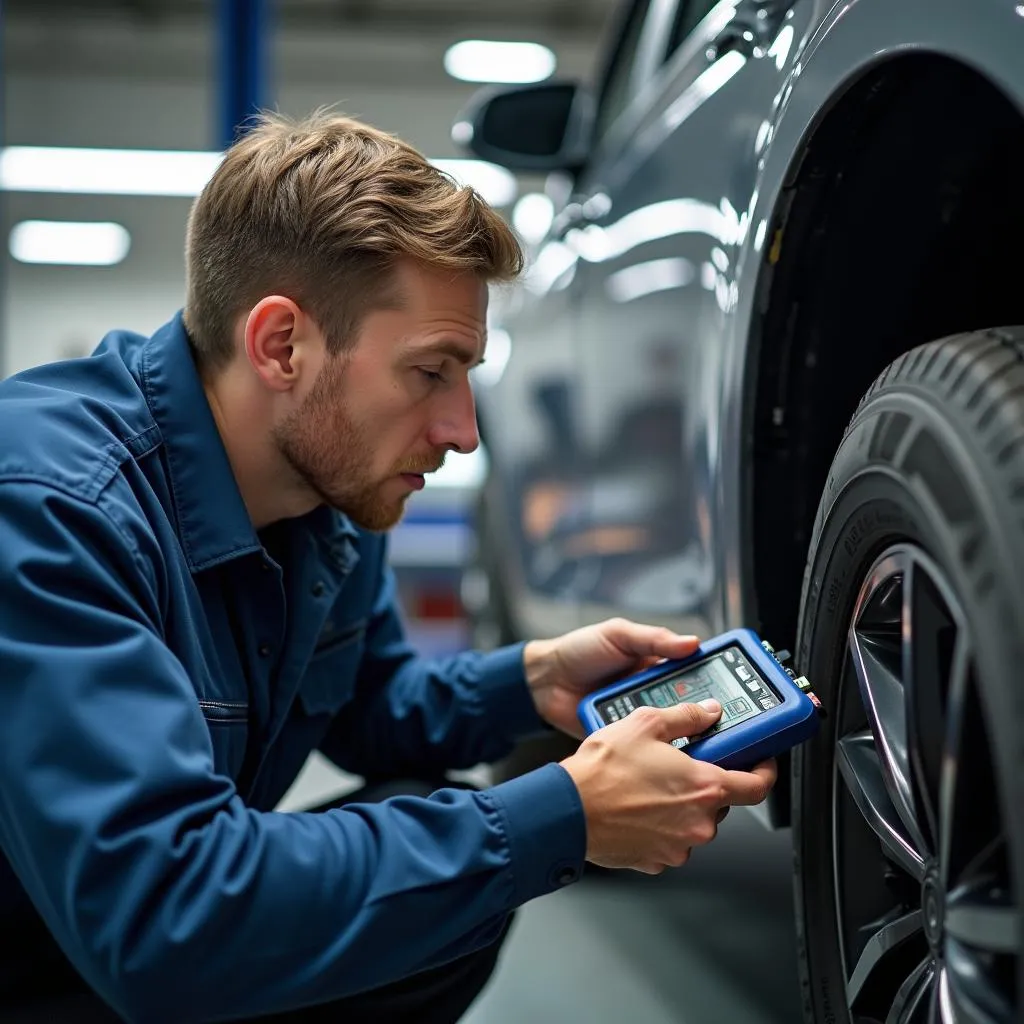 Mechanic using diagnostic tools to troubleshoot a car anti-theft system problem
Mechanic using diagnostic tools to troubleshoot a car anti-theft system problem
Troubleshooting Common Anti-theft Issues
While complex repairs are best left to professionals, here are a few troubleshooting steps you can try:
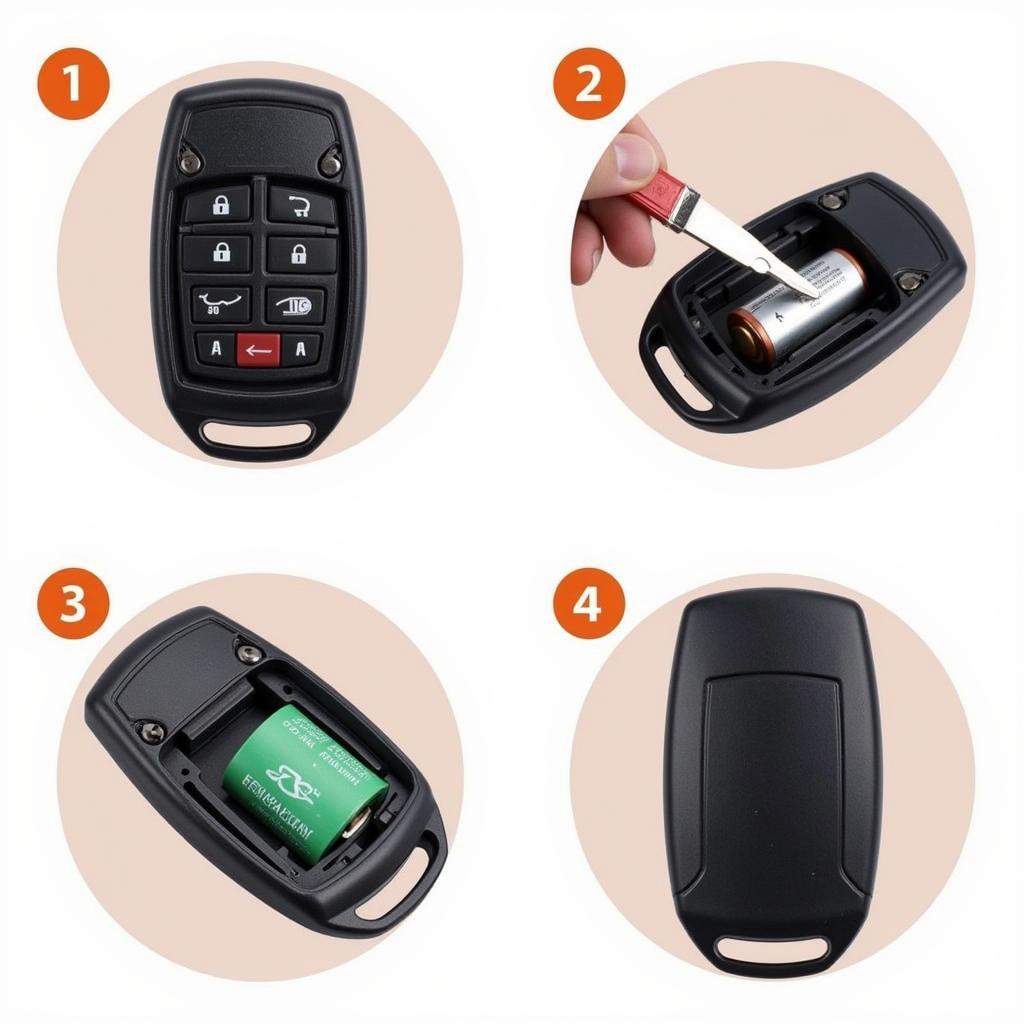
- Check Your Key Fob Battery: A weak battery can disrupt the immobilizer’s signal. Replace the battery and try again.
- Inspect Key Fob and Ignition Cylinder: Look for any signs of damage or wear. A worn-out key or cylinder can cause communication problems.
For more in-depth diagnostics and repairs, consider professional assistance. Cardiagtech offers a range of diagnostic and programming solutions for automotive anti-theft systems.
FAQs about Anti-theft Security Systems
Can I install an aftermarket anti-theft system?
Yes, many aftermarket options provide additional layers of security.
How much does an anti-theft system cost?
Costs vary widely depending on features and complexity. Factory-installed systems are typically more affordable than aftermarket options.
Can I disable my anti-theft system temporarily?
It’s not recommended to disable the system unless absolutely necessary.
For expert advice or to explore our range of diagnostic tools and software, connect with CARDIAGTECH today. We are here to help you keep your vehicle secure.

