Owning a car comes with many perks, but also the inherent risk of theft. Thankfully, modern vehicles come equipped with anti-theft deterrent systems designed to deter potential thieves and protect your car. These systems work by using a variety of electronic and mechanical components to make stealing a car much more difficult. But what exactly is an anti-theft deterrent system and how does it work?
Understanding the Basics of Anti-theft Deterrent Systems
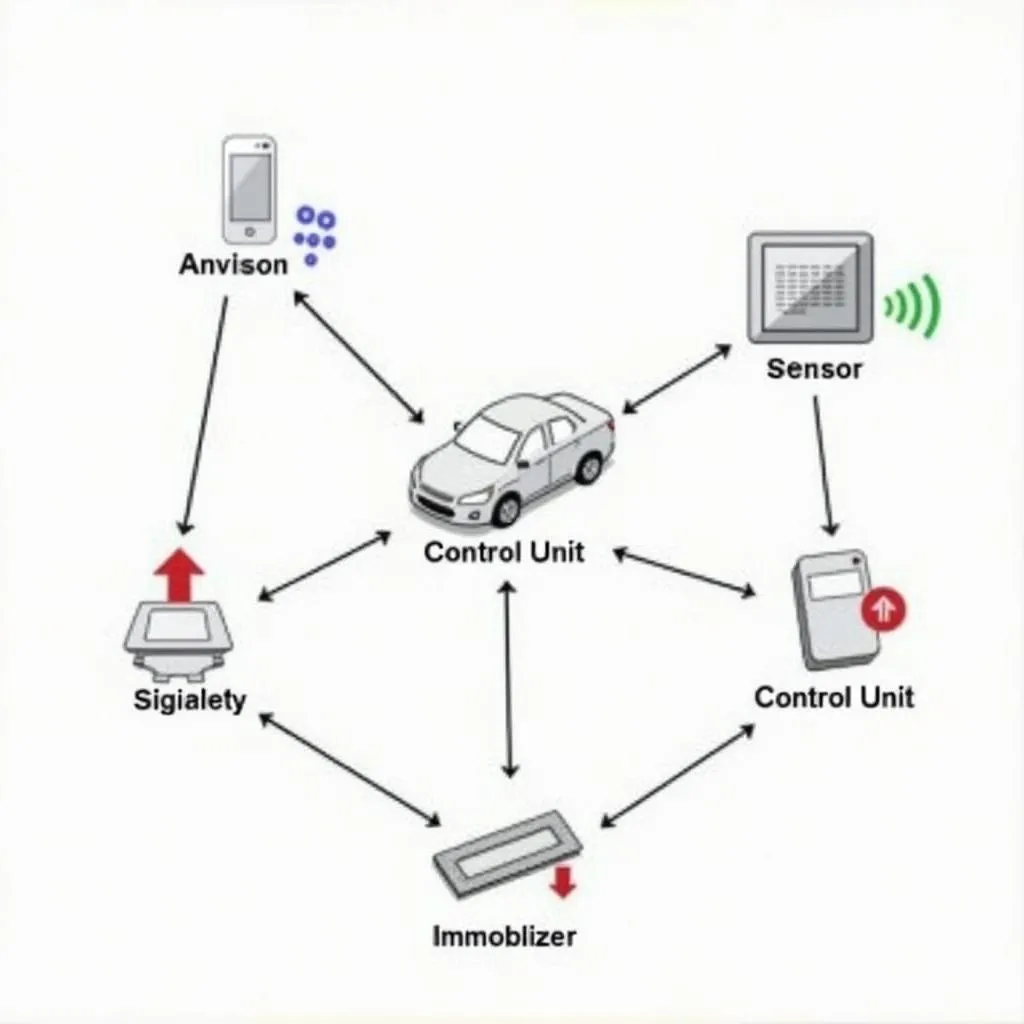
An anti-theft deterrent system, also known as a car alarm or immobilizer system, is a complex network of electronic and mechanical devices that work together to prevent car theft. These systems can vary widely in complexity, ranging from basic alarm systems to sophisticated GPS-based tracking and immobilization technologies.
Common Types of Anti-theft Deterrent Systems
There are several types of anti-theft deterrent systems available on the market, each offering a different level of protection. Some of the most common ones include:
- Immobilizers: These systems prevent the engine from starting without the correct key or key fob present. They work by disabling crucial components of the engine’s ignition system.
- Alarm Systems: Traditional car alarms use sensors to detect unauthorized entry, triggering a loud siren and flashing lights to scare off thieves and alert the owner and bystanders.
- GPS Tracking Systems: These advanced systems use GPS technology to track the location of your vehicle in real-time. In the event of theft, they can relay the car’s whereabouts to the authorities, aiding in recovery.
- Remote Keyless Entry (RKE): While primarily for convenience, RKE systems contribute to security by allowing you to lock and unlock your car from a distance, ensuring the doors are secure.
How Anti-theft Systems Work
The specific workings of an anti-theft deterrent system depend on the type of system installed. However, here’s a general overview:
- Arming the System: Most systems are armed automatically when you lock your car using the key fob or the door lock button.
- Detecting a Threat: When armed, the system’s sensors (door sensors, shock sensors, motion sensors, etc.) are on high alert for any suspicious activity.
- Triggering the Alarm: If a sensor detects a potential threat, such as someone trying to force open a door or break a window, it sends a signal to the control unit.
- Sounding the Alarm: The control unit, upon receiving a signal from a triggered sensor, activates the alarm, setting off the siren and flashing lights.
- Immobilizing the Engine (if equipped): For systems with an immobilizer, the control unit also prevents the engine from starting unless the correct key or key fob is present.
 Car anti-theft system components diagram
Car anti-theft system components diagram
Identifying Problems with Your Anti-theft System
A malfunctioning anti-theft system can be a major inconvenience, often preventing your car from starting or triggering false alarms. Here are some signs of a potential issue:
- Car Won’t Start: If your car refuses to start and you’ve ruled out other potential causes, a faulty immobilizer might be the culprit.
- Dashboard Warning Lights: Many vehicles have a dedicated warning light for the anti-theft system. If this light is on or flashing, it signals a problem.
- Erratic Alarm Behavior: False alarms, where the alarm goes off without any apparent reason, could point to a sensor malfunction or a wiring issue.
Tools for Diagnosing Anti-theft System Issues
Diagnosing problems with modern car electronics often requires specialized equipment. Here are some tools commonly used to diagnose anti-theft system issues:
- Code Readers: These handheld devices can read diagnostic trouble codes stored in your car’s computer, often pinpointing the source of the problem.
- Multimeters: A multimeter can be used to test the voltage and continuity of wiring and electrical components within the anti-theft system.
- Security System Testers: Some specialized testers are designed specifically for diagnosing problems with car alarm and immobilizer systems.
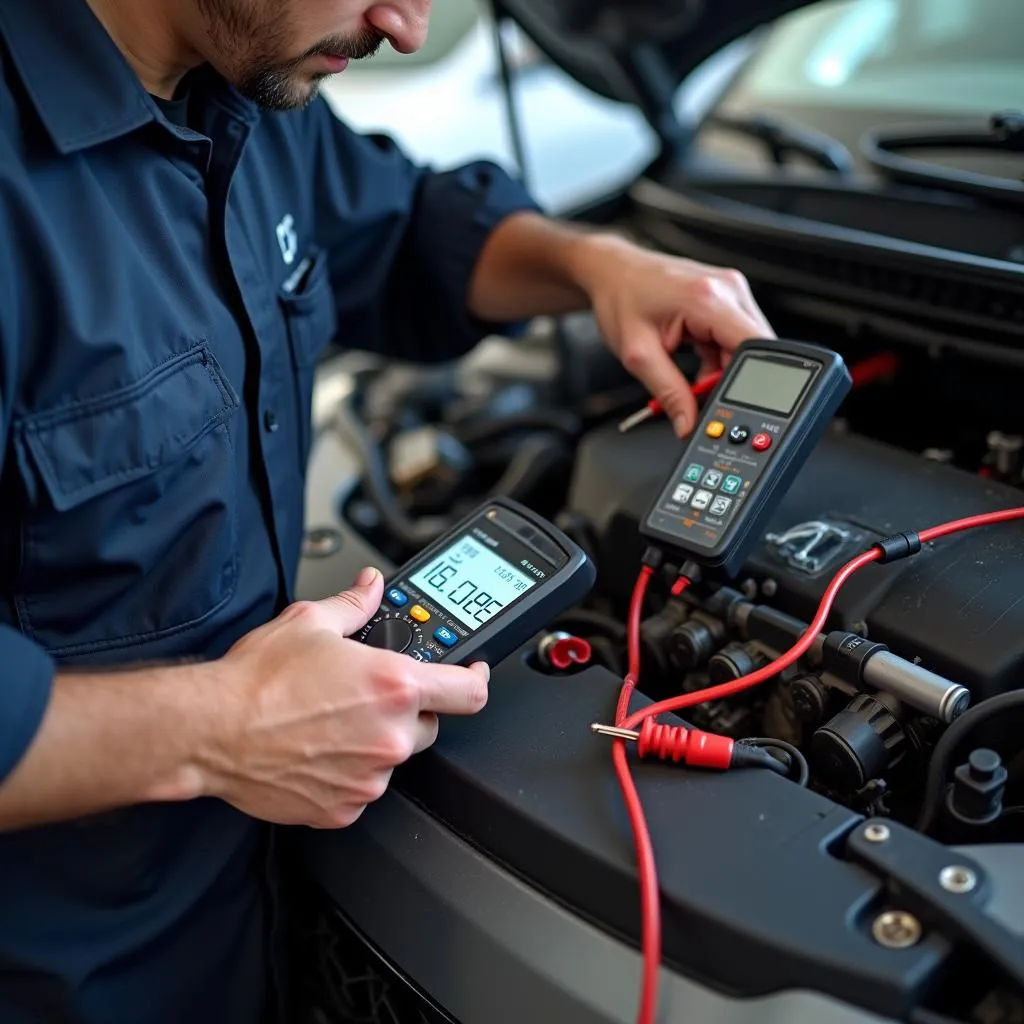 Mechanic using car diagnostic tools
Mechanic using car diagnostic tools
FAQs about Anti-theft Deterrent Systems
Q: Can I install an anti-theft system myself?
A: While some basic aftermarket systems are designed for DIY installation, it’s generally recommended to have a professional install your anti-theft system, especially for complex systems that require integration with your car’s electrical system.
Q: How can I reset my anti-theft system after a false alarm?
A: The process for resetting an anti-theft system varies depending on the car make and model. You can often reset the system by simply unlocking your car with the key fob or inserting the key in the ignition. Refer to your car’s owner’s manual for specific instructions.
Q: Can I upgrade the anti-theft system in my older car?
A: Yes, you can often upgrade the anti-theft system in your older car with aftermarket options. Many reputable brands offer a variety of systems compatible with older vehicle models.
Need Help With Your Car’s Anti-theft System?
Dealing with a malfunctioning anti-theft system can be frustrating. If you’re experiencing issues with your car’s security system, it’s essential to address them promptly. Contact CARDIAGTECH today for professional diagnostics, programming, and remote software installation services to get your car back on the road and secure again. [Link to relevant CARDIAGTECH service page].
For more information on keeping your car safe, check out our articles on Is a PASS Key Theft Deterrent System a Passive Anti-theft Device?, How to Make a Car Anti-theft, and How to Install Ring Spotlight Cam Battery Anti-theft.


