Disabling the Anti-Shudder Valve (AGR) with VCDS is a common procedure, often sought after by drivers experiencing issues related to this component. This guide dives into the intricacies of the AGR, its function, potential problems, and the process of deactivation using VCDS.
Understanding the AGR Valve and Its Purpose
The AGR valve, also known as the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve, plays a crucial role in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, a harmful byproduct of combustion. It does this by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the intake manifold, effectively lowering combustion temperatures and thus reducing NOx formation. This is particularly important for meeting stringent emission standards. However, this process can lead to issues over time.
Common Problems Associated with the AGR Valve
The recirculated exhaust gases contain soot and other particulate matter, which can gradually accumulate within the AGR valve and intake manifold. This build-up can lead to several problems, including:
- Reduced engine performance: Restricted airflow due to clogging can lead to power loss and sluggish acceleration.
- Rough idling: An improperly functioning AGR valve can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, resulting in a rough or uneven idle.
- Increased fuel consumption: The engine may compensate for reduced performance by consuming more fuel.
- Fault codes: The car’s onboard diagnostic system can detect AGR valve malfunctions and trigger fault codes, often illuminating the check engine light.
- Emission test failures: A faulty AGR can cause your vehicle to fail emissions tests.
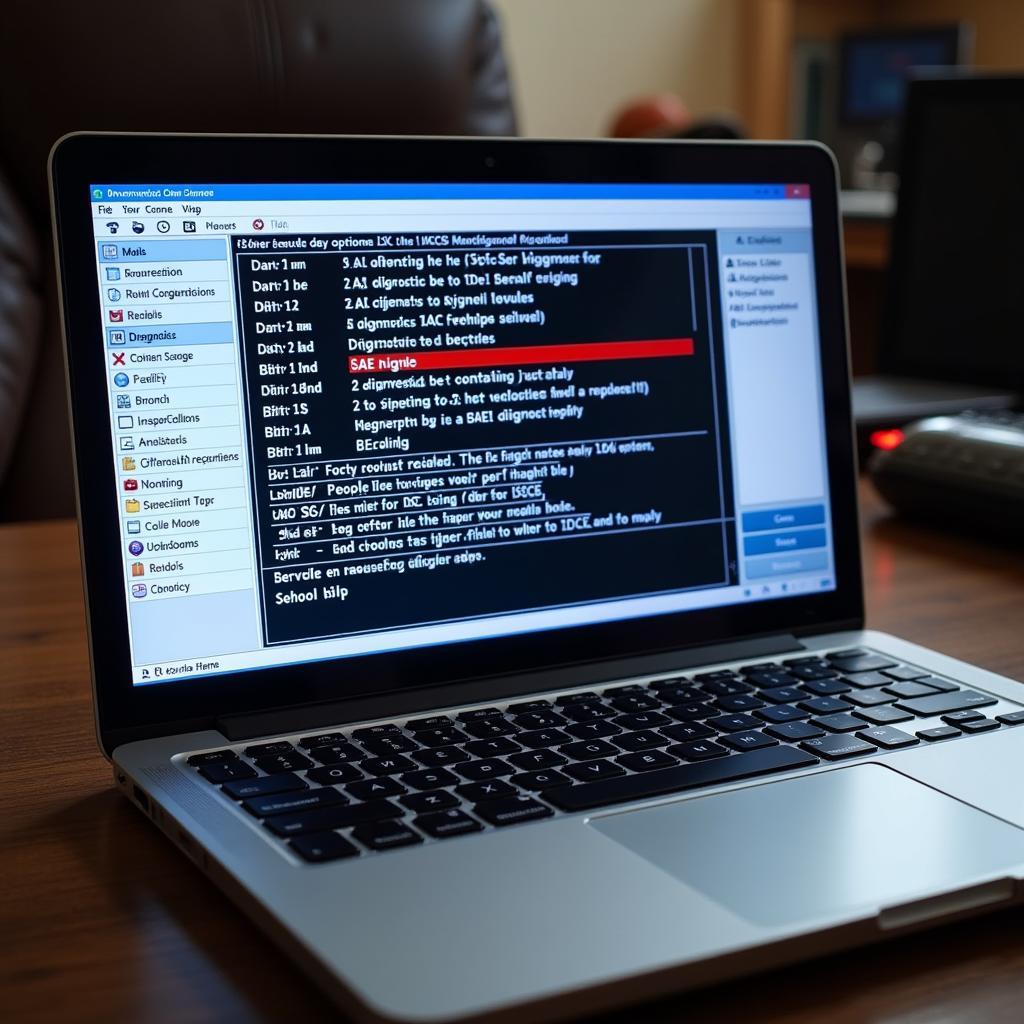
Deactivating the AGR Valve with VCDS: A Step-by-Step Guide
While cleaning the AGR valve is a temporary solution, some drivers opt to disable it completely using VCDS, a diagnostic software for Volkswagen, Audi, Seat, and Skoda vehicles. Here’s a detailed guide on how to do it:
- Connect VCDS to your vehicle’s OBD-II port. Ensure the ignition is on but the engine is not running.
- Select the “Select Control Module” option.
- Choose “Engine” (01-Engine).
- Go to “Advanced Measuring Values.”
- Locate the AGR adaptation channels. These channels vary depending on the specific engine code, so consult your vehicle’s documentation or online forums for the correct channels.
- Adjust the adaptation values to disable the AGR. Again, the specific values required for deactivation will depend on the engine code. It’s crucial to have the correct information before making any changes.
- Save the new adaptation values.
- Clear any fault codes related to the AGR valve.
Considerations Before Disabling the AGR Valve
Deactivating the AGR valve has implications that should be carefully considered:
- Emissions: Disabling the AGR valve will likely increase NOx emissions, potentially causing your vehicle to fail emissions tests.
- Legality: In many regions, tampering with emissions control systems is illegal. Check local regulations before proceeding.
- Warning Lights: While VCDS allows you to clear fault codes, the check engine light may reappear if the ECU detects other related issues.
- Long-term Effects: While often negligible, there might be unknown long-term consequences for your specific engine.
“Disabling the AGR can be a viable solution for persistent issues, but it’s essential to understand the potential drawbacks and legal ramifications,” says John Miller, a senior automotive diagnostic technician at EuroTech Garage.
Alternative Solutions to AGR Issues
Before resorting to deactivation, consider these alternatives:
- AGR Valve Cleaning: Thorough cleaning can restore functionality, albeit temporarily.
- AGR Valve Replacement: A new AGR valve can resolve issues caused by a faulty component.
- Professional Diagnosis: Consult a qualified technician to diagnose the root cause of the problem.
Conclusion
Disabling the AGR valve with VCDS can be a solution for recurring problems, but it’s important to weigh the pros and cons and understand the potential legal and environmental implications. Always research your specific vehicle and engine code before making any modifications. If you’re unsure, consult a qualified automotive technician. Remember, understanding the AGR system is key to making an informed decision about its management.
FAQ
- What does AGR stand for? AGR stands for Anti-Shudder Valve, also known as the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve.
- Why would I disable the AGR valve? You might disable the AGR valve to address persistent issues like clogging, rough idling, or reduced engine performance.
- Is it legal to disable the AGR valve? The legality of disabling the AGR valve varies by region. Check local regulations before proceeding.
- What are the alternatives to disabling the AGR valve? Alternatives include cleaning the AGR valve, replacing it, or seeking professional diagnosis.
- What software do I need to disable the AGR valve? You will need VCDS software, a diagnostic tool for VAG vehicles.
- Can disabling the AGR valve cause my car to fail emissions tests? Yes, disabling the AGR valve is likely to increase NOx emissions and could cause your vehicle to fail emissions tests.
- What are the long-term effects of disabling the AGR valve? While often negligible, there might be unknown long-term consequences for your specific engine. Consult a professional for advice.
For further assistance, please contact us via Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, Email: CARDIAGTECH[email protected] or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Our customer service team is available 24/7. We also offer other diagnostic and programming services. Check out our other articles on related topics such as DPF regeneration and ECU tuning.