A fully charged battery that fails to crank your engine can be incredibly frustrating. This situation, often described as “battery charged but no cranking power,” indicates a problem beyond a simple dead battery. This guide dives deep into the potential causes, diagnostic steps, and solutions for this common car issue.
 Car Battery Showing Full Charge But Engine Won't Crank
Car Battery Showing Full Charge But Engine Won't Crank
One common culprit is a faulty starter motor. If the starter is failing, it won’t be able to engage the engine, even with a fully charged battery. You might hear a clicking sound when you turn the key, indicating the starter solenoid is engaging, but the motor itself isn’t turning. Check out this helpful guide if your car completely dead with new battery.
Understanding the Problem: Why a Charged Battery Might Not Crank
Having a charged battery doesn’t guarantee a starting engine. The cranking process requires a significant electrical current to turn the engine over. Several components can disrupt this process, even with a fully charged battery. These include the starter motor, starter solenoid, ignition switch, and electrical connections.
Common Causes of “Battery Charged But No Cranking Power”
- Faulty Starter Motor: As mentioned, a bad starter is a frequent cause.
- Bad Starter Solenoid: This component acts as a relay, switching the high current needed to power the starter motor.
- Corroded or Loose Battery Terminals: A poor connection can prevent sufficient current flow.
- Damaged or Corroded Wiring: Wiring issues can interrupt the electrical circuit to the starter.
- Faulty Ignition Switch: The ignition switch supplies power to the starter circuit. A malfunction can prevent the starter from receiving power.
- Blown Fuses or Relays: A blown fuse or relay in the starter circuit will interrupt power flow.
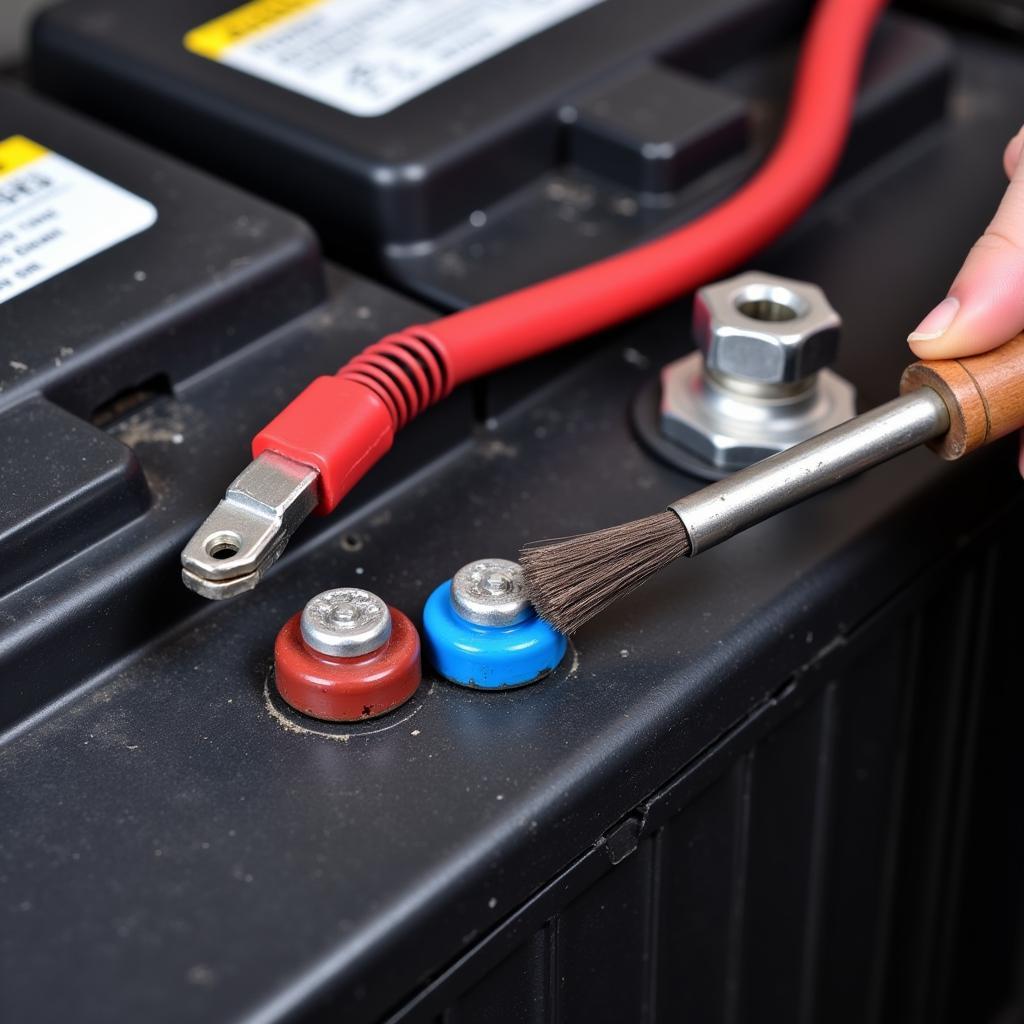
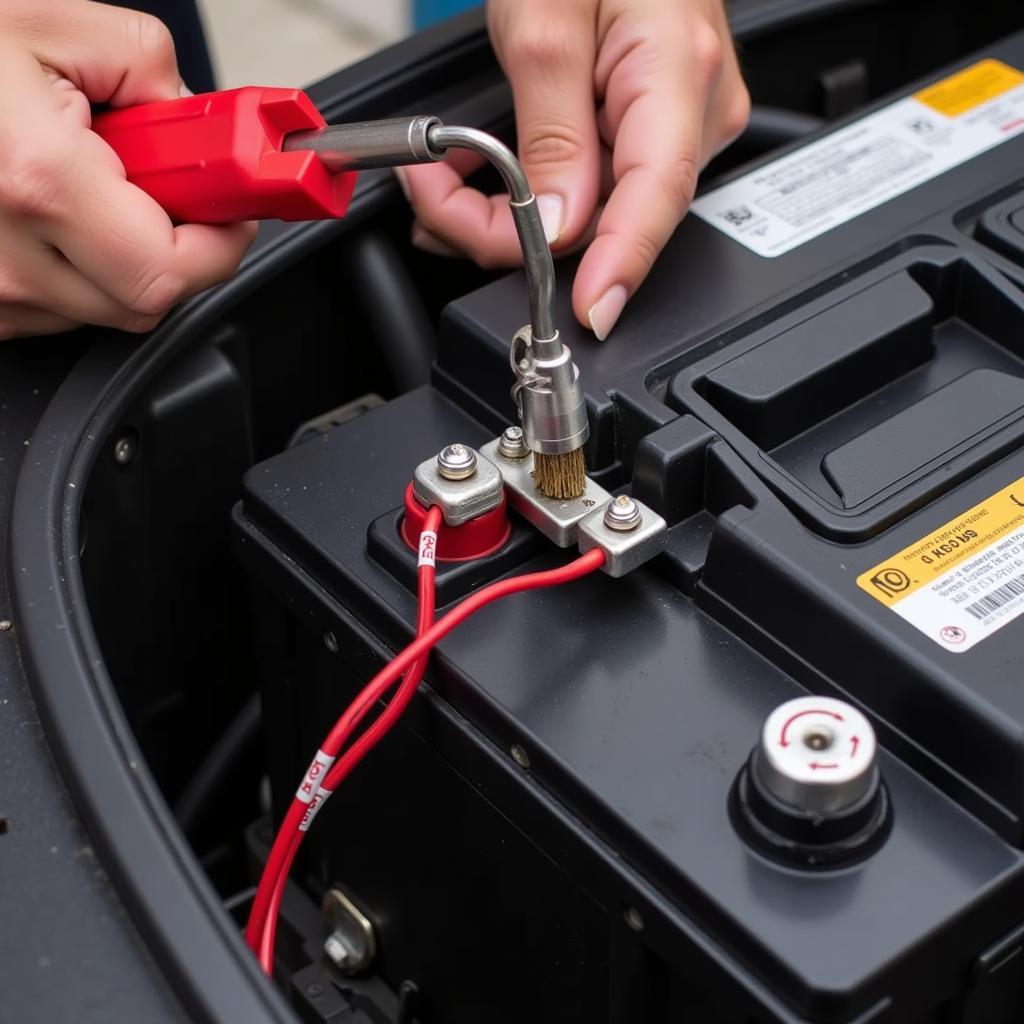 Inspecting Battery Terminals for Corrosion and Secure Connection
Inspecting Battery Terminals for Corrosion and Secure Connection
“Always start by checking the simplest things first, like the battery terminals. You’d be surprised how often a loose or corroded connection is the culprit,” advises John Miller, a seasoned automotive electrical technician with over 20 years of experience.
Diagnosing the Problem: Step-by-Step Guide
- Check Battery Terminals: Inspect and clean the battery terminals and cable connections for any corrosion or looseness.
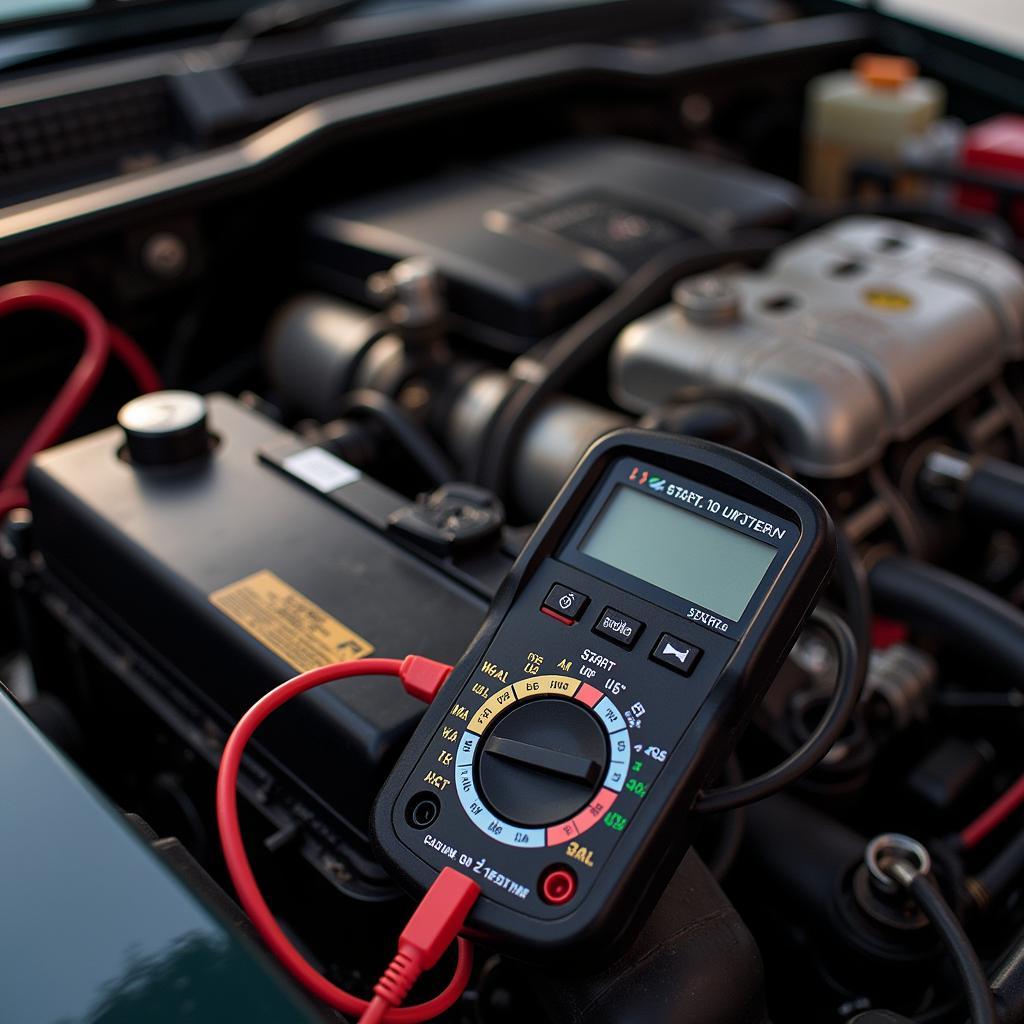
- Test the Battery Voltage: Even if the battery appears charged, verify its voltage with a multimeter. It should read around 12.6 volts. For more insights, read about scenarios where your car completely dead no power new battery.
- Test the Starter: Use a multimeter or test light to check for voltage at the starter solenoid when the key is turned to the “start” position.
- Inspect Wiring and Connections: Carefully examine the wiring and connections between the battery, starter, and ignition switch for any damage or corrosion.
Using a Multimeter for Diagnosis
A multimeter is a valuable tool for diagnosing electrical issues. It can be used to test battery voltage, starter voltage, and continuity in the wiring.
Solutions and Repairs
The solution depends on the diagnosed cause. This could range from simple cleaning of battery terminals to replacing the starter motor or other components.
- Clean Battery Terminals: Use a wire brush and baking soda solution to clean corroded terminals.
- Tighten Connections: Ensure all battery cables and connections are securely tightened.
- Replace Faulty Components: Replace any faulty components, such as the starter, solenoid, ignition switch, or damaged wiring. Consider reading this if your car wont start with good battery.
“While some repairs can be done DIY, complex electrical issues are best left to professionals,” recommends Sarah Chen, an automotive electrical engineer with extensive experience in vehicle diagnostics.
Conclusion: Getting Your Car Started
Experiencing “battery charged but no cranking power” can be a perplexing issue. However, by systematically checking the key components and using diagnostic tools like a multimeter, you can identify the root cause and get your car back on the road. Don’t forget to check resources like this article discussing jaguar f type low battery please start engine for specific car model issues. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to electrical issues can prevent this problem and ensure your car starts reliably every time. Remember, even a fully charged battery isn’t a guarantee against cranking problems.
FAQ
- Can a bad alternator cause no cranking power? While a bad alternator won’t directly prevent cranking, it can drain the battery, eventually leading to no cranking power.
- What does a clicking sound when trying to start the car mean? A clicking sound often indicates a problem with the starter solenoid or low battery voltage. You might want to reference information about 6 v ford car radio wiring diagrams if your vehicle is older.
- How much does it cost to replace a starter? The cost varies depending on the car make and model, but typically ranges from $200 to $500.
- Can I jump-start a car with a charged battery but no cranking power? Jump-starting likely won’t help if the problem is with the starter, solenoid, or wiring.
- How can I prevent this problem in the future? Regular battery maintenance, cleaning terminals, and inspecting wiring can help prevent future cranking issues.
- What if I’ve checked everything and still have no cranking power? Consult a qualified automotive electrician for further diagnosis and repair.
- Could extreme temperatures affect cranking power, even with a charged battery? Yes, extreme cold can thicken engine oil and increase the load on the starter, making it harder to crank. Extreme heat can also affect battery performance.


