The dreaded brake system warning light on your Toyota Sienna can be a heart-stopper, but don’t panic! It doesn’t always mean a complete brake failure is imminent. Understanding what triggers this light and how to troubleshoot it can save you time, money, and unnecessary worry. This comprehensive guide delves into the common causes of the brake system warning light in Toyota Sienna vans and provides practical solutions for a safe and smooth driving experience.
Common Causes of a Brake System Warning Light in Toyota Sienna
The brake system warning light in your Sienna can illuminate for several reasons, some more serious than others. Here’s a breakdown of the most common culprits:
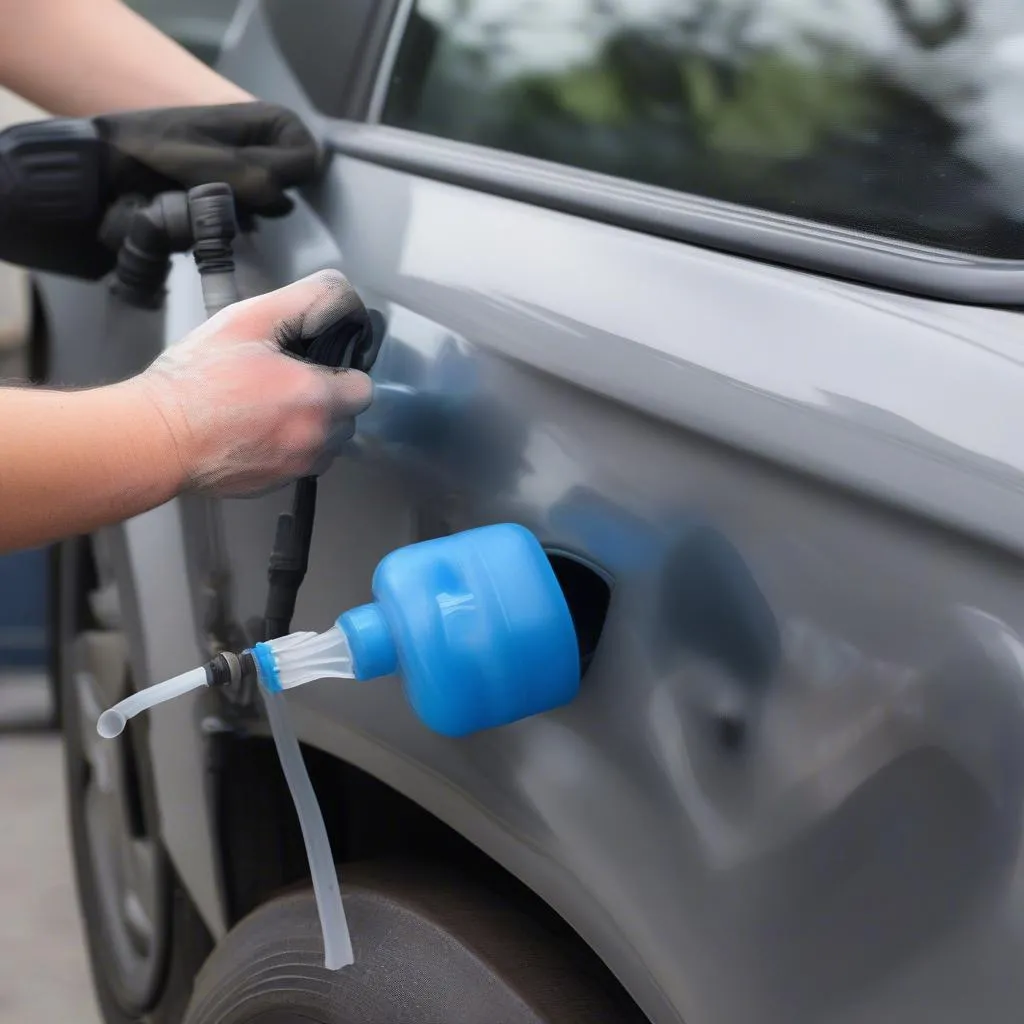
1. Low Brake Fluid Level
This is the most frequent cause of the brake system warning light. Brake fluid, responsible for transmitting force from the brake pedal to the wheels, can decrease over time due to leaks or wear and tear in brake components.
Solution:
- Check your brake fluid reservoir. Park your Sienna on a level surface and locate the brake fluid reservoir under the hood. The reservoir usually has a translucent container with minimum and maximum level markings.
- Inspect the fluid level. If it’s below the minimum mark, your brake system warning light is likely triggered.
- Add brake fluid (if necessary). Carefully remove the reservoir cap and add the recommended brake fluid for your Sienna model.
- Address any leaks. If the fluid level is consistently low, you might have a leak in your brake lines, calipers, or wheel cylinders. It’s crucial to have a professional mechanic diagnose and repair the leak promptly.
2. Worn Brake Pads
Brake pads are designed to wear down over time. When they reach a certain thinness, a sensor embedded within the pad contacts the rotor, triggering the brake system warning light.
Solution:
- Inspect your brake pads. Look through the spaces between the spokes of your wheels. You might be able to get a visual of the brake pad’s outer pad and the metal wear indicator.
- Replace worn brake pads. If your pads are nearing the wear limit or the wear indicator is touching the rotor, it’s time for a replacement.
Expert Insight from John Miller, ASE Certified Master Technician:
“Ignoring worn brake pads not only compromises your safety but can also lead to expensive rotor damage. It’s always best to address brake pad replacement proactively.”
3. Faulty Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch, located behind the brake pedal, activates your brake lights when you press the pedal. A malfunctioning switch can disrupt this signal and illuminate the brake system warning light.
Solution:
- Test your brake lights. Have someone observe the brake lights while you press the brake pedal. If the lights don’t illuminate, a faulty brake light switch is a likely cause.
- Replace the brake light switch. This task usually involves removing the panel under the steering wheel to access and replace the switch.
4. ABS Issues
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) prevents wheel lockup during hard braking, ensuring steering control. If the ABS system encounters a problem, the brake system warning light will turn on.
Solution:
- Check for stored ABS codes. A professional mechanic can use a diagnostic scanner to retrieve any stored ABS codes, pinpointing the specific issue.
- Address the underlying ABS problem. Depending on the diagnostic codes, the mechanic can repair or replace faulty ABS components like wheel speed sensors, ABS modules, or wiring harnesses.
5. Other Potential Causes
While less common, other factors like a faulty parking brake switch, issues with the master cylinder, or problems within the vehicle’s electrical system can also trigger the brake system warning light.
Expert Tip:
“Don’t ignore the brake system warning light, even if your brakes seem to be functioning normally. Early diagnosis can prevent minor issues from escalating into major and costly repairs.” – Sarah Thompson, Certified Automotive Technician
What to Do When Your Brake System Warning Light Comes On
- Don’t Panic. Pull over to a safe location as soon as possible.
- Check Your Owner’s Manual. Consult your Sienna’s owner’s manual for specific instructions and recommendations related to the brake system warning light.
- Inspect Brake Fluid Level. If the fluid is low and you have brake fluid on hand, carefully top it off.
- Avoid Driving (If Possible). If the warning light persists or you notice any changes in brake pedal feel or performance, avoid driving and contact a qualified mechanic for immediate inspection.
Conclusion
The brake system warning light in your Toyota Sienna should never be ignored. By understanding the common causes and taking appropriate action, you can ensure your safety and keep your Sienna running smoothly for miles to come. Remember, early detection and prompt repairs are always the best course of action when it comes to brake system issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I drive my Toyota Sienna with the brake system warning light on? It’s highly discouraged. Driving with the brake system warning light on can be dangerous and potentially lead to further damage.
- How much does it cost to fix a brake system warning light on a Toyota Sienna? The cost varies significantly depending on the underlying cause. A simple brake fluid top-up might cost under $20, while brake pad replacement can range from $150 to $300 per axle. More complex repairs like ABS module replacement can cost upwards of $1000.
- How often should I check my Toyota Sienna’s brake fluid level? It’s a good practice to check your brake fluid level at least once a month and before long trips.
- Can I add any brake fluid to my Toyota Sienna? No, always use the brake fluid type recommended in your Sienna’s owner’s manual.
- How often should I get my Toyota Sienna’s brakes inspected? It’s generally recommended to have your brakes inspected annually or every 12,000 miles, whichever comes first.
Internal Links:
- Concerned about brake pad warnings? Learn more about the mini brake pads warning light.
- For specific instructions on clearing a 2011 Toyota Sienna brake warning light, check out our guide on how to clear 2011 toyota sienna brake warning light.
- Experiencing brake warning light issues with your 2000 Toyota Sienna? We have information available for the 2000 toyota sienna brake warning light.
- If you own a 2004 Sienna, find insights related to the 2004 sienna brake warning light.
- Learn about common causes and solutions for the 2001 toyota sienna brake warning light.