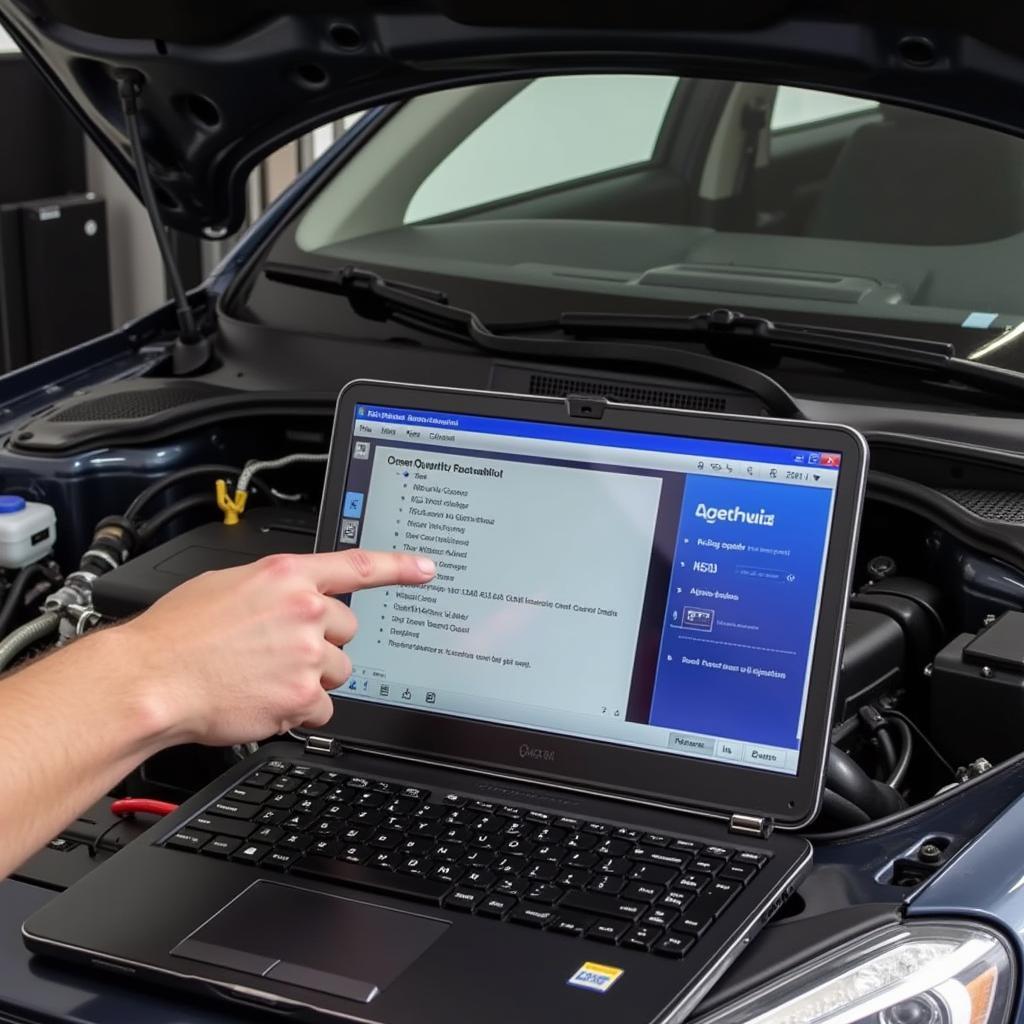
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is a crucial component of modern diesel engines, especially the 2.0 TDI found in many Volkswagen Audi Group (VAG) vehicles. It functions by redirecting a portion of exhaust gases back into the intake manifold, effectively reducing combustion temperatures and NOx emissions. Like many engine systems, the EGR system requires periodic adaptation using a diagnostic tool like VCDS (Vag-Com Diagnostic System). This article delves into the intricacies of EGR adaptation on 2.0 TDI engines using VCDS, providing a detailed walkthrough for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
What is EGR Adaptation and Why is it Important?
EGR adaptation is the process of calibrating the engine control unit (ECU) to recognize the EGR valve’s position and operation across its range. This process is vital for several reasons:
- Optimal EGR Flow: Ensures the correct amount of exhaust gas is recirculated for emission control without compromising engine performance.
- Preventing Fault Codes: An incorrectly adapted EGR system can trigger fault codes in the ECU, potentially leading to limp mode or other driveability issues.
- Smooth Engine Operation: Proper adaptation helps maintain smooth idle, linear throttle response, and overall engine efficiency.
When to Perform EGR Adaptation on a 2.0 TDI Engine
Several scenarios might necessitate EGR adaptation on a 2.0 TDI engine:
- EGR Valve Cleaning or Replacement: After cleaning or replacing the EGR valve, adaptation is essential to re-establish proper communication between the valve and the ECU.
- Fault Codes Related to EGR: If fault codes related to EGR flow, position, or performance are present, performing an adaptation can potentially resolve them.
- Rough Idle or Poor Performance: If a 2.0 TDI engine exhibits rough idle, hesitant acceleration, or decreased fuel economy, an EGR adaptation might be necessary to rule out EGR-related issues.
EGR Adaptation Procedure using VCDS
Before initiating the adaptation, it’s crucial to ensure the following:
- Engine is at Operating Temperature: The engine needs to be warm, ideally after a 15-20 minute drive.
- No Fault Codes Present: Clear any existing fault codes related to the EGR system before starting the adaptation.
- Battery Support Recommended: Connecting a battery charger or jump starter is recommended to maintain stable voltage during the process.
Steps for EGR Adaptation using VCDS:
- Connect VCDS to the OBD-II Port: Locate the OBD-II port on your 2.0 TDI vehicle, usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side, and connect the VCDS interface cable.
- Launch VCDS Software: Turn on the ignition (do not start the engine) and launch the VCDS software on your computer.
- Select Control Module: Navigate to “Select Control Module” and choose “Engine” from the list.
- Access Basic Settings: Within the Engine module, go to “Basic Settings”
- Select EGR Adaptation Channel: Locate the channel related to “EGR Adaptation” or “EGR System Adaptation.” The specific channel number may vary slightly depending on the engine code and model year.
- Initiate Adaptation: Follow the on-screen prompts in VCDS to start the adaptation process. The software will guide you through the necessary steps, which usually involve running the engine at specific RPMs for a set duration.
- Verify Successful Adaptation: Once the process is complete, VCDS will indicate if the adaptation was successful. If successful, clear any fault codes, and you’re good to go. If the adaptation fails, there might be an underlying issue with the EGR system requiring further diagnosis and repair.
 EGR Valve on Engine
EGR Valve on Engine
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While EGR adaptation is generally straightforward, encountering issues is possible. Here are some common problems and potential solutions:
- Adaptation Not Starting: Ensure the engine is at operating temperature, all fault codes are cleared, and the battery voltage is stable.
- Adaptation Fails Mid-Process: This could indicate a faulty EGR valve, a problem with the EGR cooler, or an issue with the wiring harness. Further diagnosis is required.
- Fault Codes Return After Adaptation: This suggests a persistent issue with the EGR system that needs to be addressed before a successful adaptation can occur.
Tips and Precautions
- Always refer to the factory repair manual for your specific 2.0 TDI engine code and model year for accurate adaptation procedures and channel numbers.
- Using a genuine VCDS interface cable and licensed software is crucial for safe and effective communication with the ECU.
- If unsure about any step, consult with a qualified automotive technician experienced in VAG vehicles and VCDS diagnostics.
 VCDS Software Interface
VCDS Software Interface
Conclusion
EGR adaptation is a critical maintenance procedure for 2.0 TDI engines, ensuring optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and compliance with emissions standards. By understanding the process, recognizing the symptoms of adaptation issues, and following the correct steps using VCDS, you can maintain the health and longevity of your 2.0 TDI engine. Remember, if you’re ever uncertain about performing this procedure yourself, seeking assistance from a qualified technician is always recommended.
For further support and a comprehensive range of automotive diagnostic tools, connect with CARDIAGTECH. We offer top-of-the-line equipment and expert guidance to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.


