We’ve all seen them: those small, often brightly colored stickers adhered to products in stores. They may seem unassuming, but these anti-theft stickers play a crucial role in deterring shoplifting. Ever wondered, “how do anti-theft stickers work?” This article delves into the fascinating technology behind these security measures.
Decoding Anti-Theft Stickers: More Than Meets the Eye
Anti-theft stickers, also known as EAS (Electronic Article Surveillance) tags, utilize various technologies to protect merchandise. These seemingly simple stickers can be surprisingly sophisticated.
Radio Frequency (RF) Tags
One of the most common types of anti-theft stickers is RF tags. These tags consist of a tiny microcircuit and an antenna, powered by a small capacitor. When exposed to the electromagnetic field generated by the detectors at store exits, the circuit resonates, emitting a unique radio frequency signal. This signal is then detected by the security system, triggering an alarm.
Acousto-Magnetic (AM) Tags
Another prevalent type is AM tags. These tags work on a different principle, using a strip of amorphous metal. When this metal strip passes through the security gates, it resonates at a specific frequency when excited by a low-frequency magnetic pulse. This resonance is picked up by the detectors, setting off the alarm.
Identifying the Silent Guardian: Types of Anti-theft Stickers
Anti-theft stickers come in various shapes and sizes, often disguised to blend in with product packaging.
The Visible Deterrent: Stickers and Labels
These are the most common anti-theft stickers, clearly visible on products. They act as a visual deterrent, discouraging potential shoplifters.
The Stealth Protectors: Concealed Tags
Some tags are designed for discreetness. These might be embedded within the product packaging or even placed under the product label, making them difficult to detect and remove.
The Mechanics of Detection: How Anti-theft Systems Work
Anti-theft systems typically comprise three main components:
The Tag: The Silent Alarm
As mentioned earlier, the tags themselves contain the technology that triggers the alarm.
The Detection System: The Gatekeeper
Security gates installed at store exits house antennas that generate electromagnetic fields (for RF tags) or magnetic pulses (for AM tags). These fields interact with the tags, triggering them to emit their signals.
The Alarm System: The Final Warning
When the detectors pick up the signals from activated tags, the alarm system is triggered. This could be an audible alarm, a flashing light, or a silent alert to store personnel.
Beyond Shoplifting: Other Applications of Anti-theft Stickers
While primarily used for retail security, the technology behind anti-theft stickers finds applications in other areas as well.
Library Security
Libraries use these tags to prevent theft of books and other materials.
Asset Tracking
Businesses can use anti-theft tags to track valuable equipment and inventory.
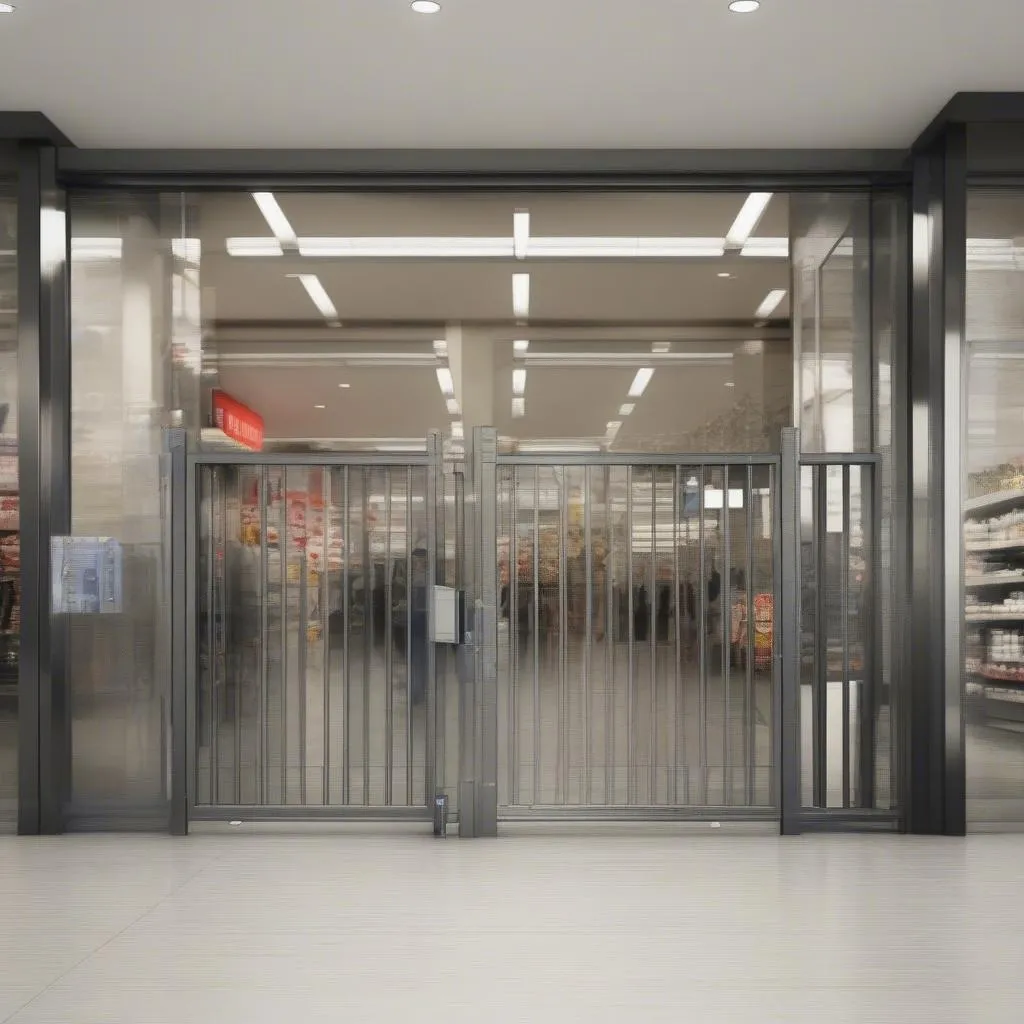 An anti-theft security gate at the exit of a retail store
An anti-theft security gate at the exit of a retail store
FAQs: Unraveling Common Queries about Anti-theft Stickers
Q: Can anti-theft stickers damage electronic devices?
A: No, anti-theft stickers use low-frequency signals that are safe for electronic devices. They will not interfere with their functionality.
Q: Can I remove anti-theft stickers at home?
A: Attempting to remove anti-theft stickers at home is not recommended and could damage the product. Retailers use specialized deactivators and detachers to safely remove these tags.
Q: Are all anti-theft stickers the same?
A: No, there are different types of anti-theft stickers, each with its own working mechanism. RF tags and AM tags are two of the most common types.
For specialized diagnostics and solutions for your vehicle’s electronic and software systems, consult the experts at CARDIAGTECH. We offer cutting-edge diagnostic tools and software to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
If you’re interested in learning more about removing anti-theft devices, you can find helpful information on our website: How to Remove Store Anti-Theft Device.