Have you ever wondered how those little tags attached to merchandise in stores prevent theft? They might seem simple, but anti-theft tags are actually based on some pretty clever technology. This article will delve into the fascinating world of anti-theft tags, explaining their different types and how they function to protect merchandise.
Understanding Different Types of Anti-Theft Tags
While they come in various shapes and sizes, anti-theft tags predominantly operate on two main technologies:
1. Radio Frequency (RF) Tags
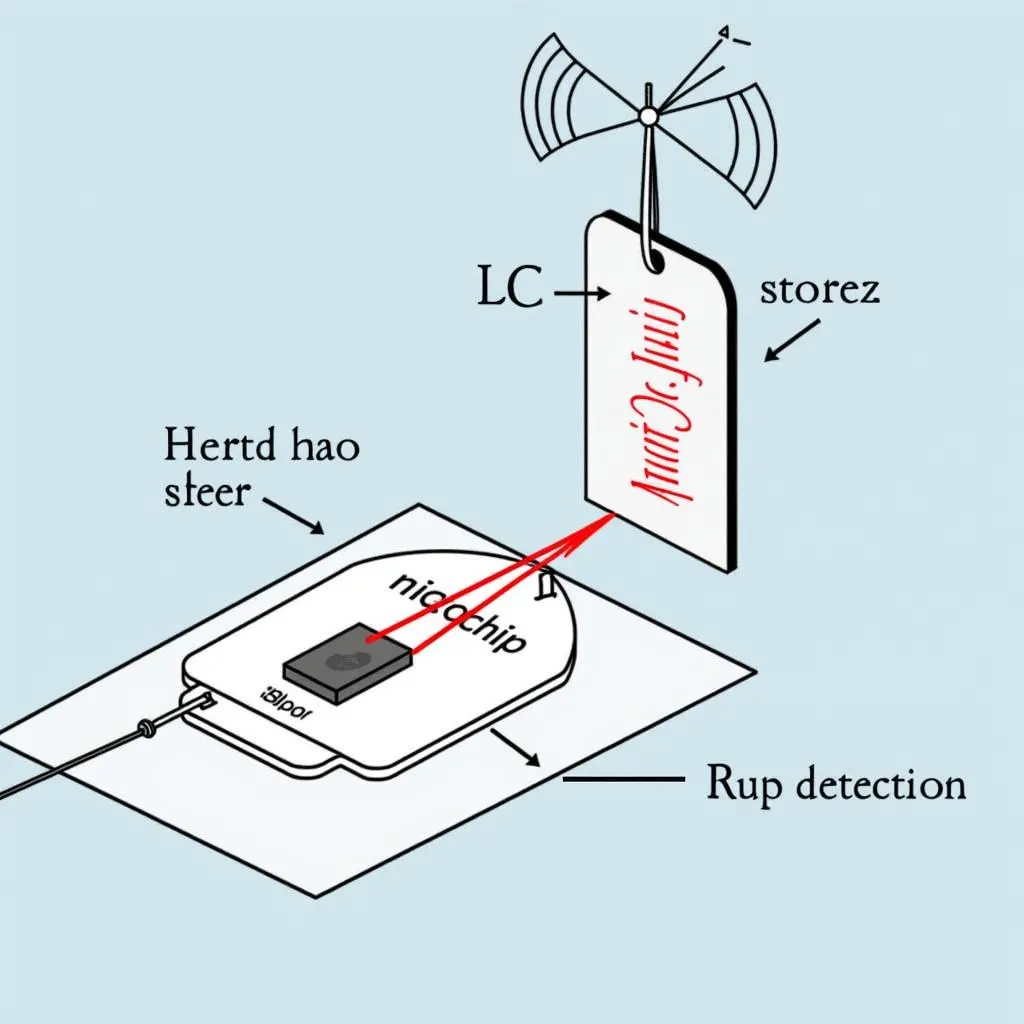
RF tags are the most common type you’ll encounter. These tags consist of a microchip and an antenna circuit, forming a simple LC circuit (inductor-capacitor circuit).
How they work:
- Activation: When an item is tagged, the RF tag is activated.
- Detection: At the store’s exit, detection systems emit radio waves within a specific frequency range. When an active RF tag passes through this field, the tag’s antenna resonates with the radio waves, inducing a small current in the LC circuit. This current activates the microchip, causing it to transmit a unique identification signal back to the detection system.
- Alarm: If the tag hasn’t been deactivated at checkout, the system interprets the tag’s signal as an attempted theft and triggers an alarm.
 RF Anti-theft Tag Diagram
RF Anti-theft Tag Diagram
2. Acousto-Magnetic (AM) Tags
AM tags are reusable and typically used for more expensive items. They utilize a different approach involving two strips: a magnetostrictive strip and a ferromagnetic strip.
How they work:
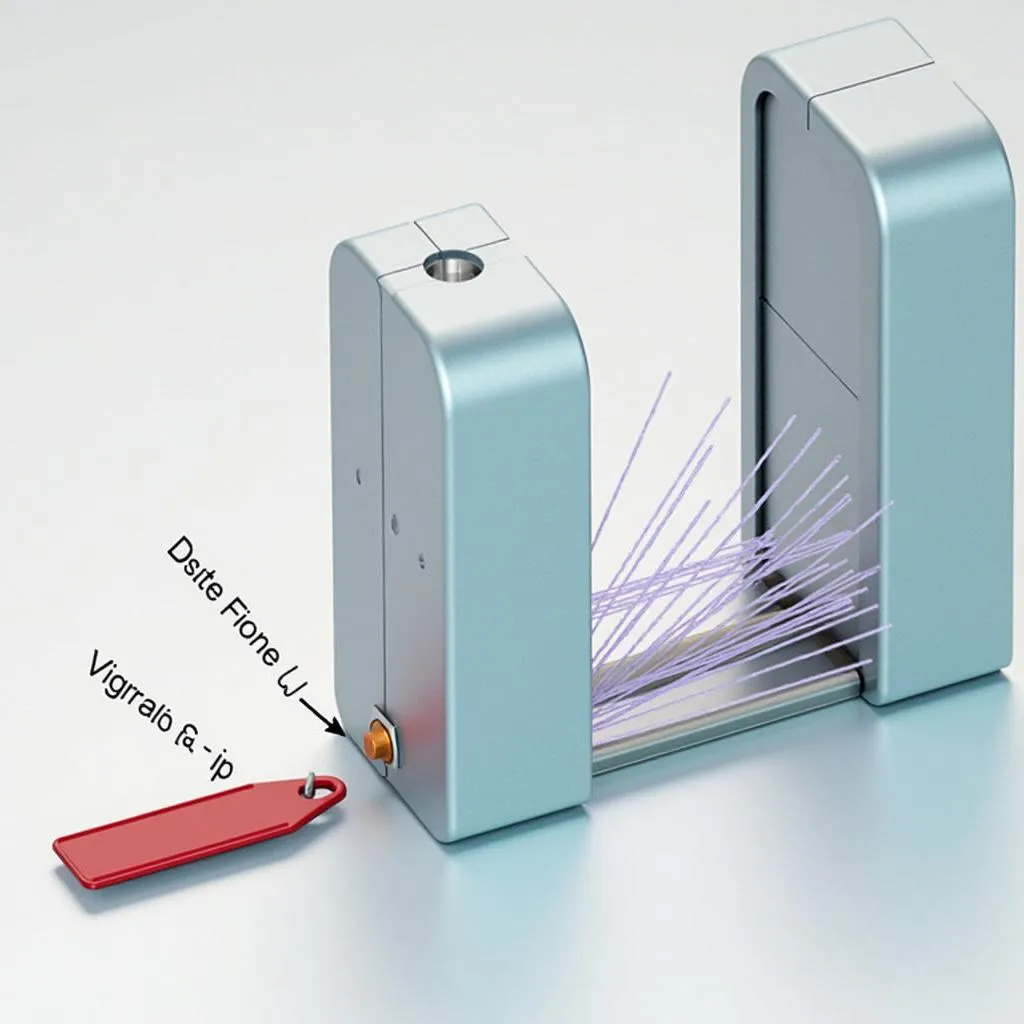
- Detection: The detection system emits a low-frequency electromagnetic pulse at regular intervals. This pulse magnetizes the ferromagnetic strip in the tag.
- Resonance: The magnetized strip interacts with the magnetostrictive strip, causing it to vibrate at a specific frequency, essentially creating a unique acoustic signature.
- Alarm: The detection system listens for this specific acoustic signature. If detected, it interprets it as an active tag and triggers an alarm.
 Acousto-Magnetic Tag Detection
Acousto-Magnetic Tag Detection
Deactivating Anti-Theft Tags at Checkout
When you purchase an item, the cashier deactivates the tag to prevent the alarm from triggering.
- RF tags: Deactivation involves disrupting the LC circuit’s ability to resonate with the detection system’s radio waves. This can be done by passing the tag over a deactivation pad that emits a strong electromagnetic pulse, or, in some cases, by physically puncturing a part of the circuit.
- AM tags: Deactivation is achieved by demagnetizing the ferromagnetic strip using a strong magnetic field at the checkout counter.
FAQs about Anti-Theft Tags
1. Can anti-theft tags damage my credit cards?
While RF tags do emit radio waves, the signal strength is very low and unlikely to damage credit cards. However, it’s always a good practice to keep them separate from your cards as a precaution.
2. Can I reuse anti-theft tags?
RF tags are usually designed for single use and are deactivated or destroyed upon purchase. AM tags, on the other hand, are designed to be reusable.
3. Can anti-theft tags be bypassed?
While there are methods circulating online claiming to bypass anti-theft tags, they are often unreliable and may even damage the merchandise.
 Different Anti-theft Tag Types
Different Anti-theft Tag Types
Conclusion
Anti-theft tags play a crucial role in retail security, protecting businesses from losses and ensuring customers have access to fairly priced goods. Understanding how these tags function provides insight into the technological advancements that safeguard our shopping experiences.
If you’re interested in exploring advanced automotive diagnostic and programming tools, visit CARDIAGTECH for cutting-edge solutions designed for today’s vehicles.


