Understanding fuel trims is crucial for diagnosing and fixing vehicle performance issues. VCDS (Vag-Com Diagnostic System) offers a powerful tool for accessing and interpreting this valuable data. This guide will walk you through how to read fuel trims VCDS, explaining their significance and providing practical tips for troubleshooting common problems.
Understanding Fuel Trims and Their Importance
Fuel trims represent adjustments made by the engine control unit (ECU) to maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio. The ECU constantly monitors oxygen sensor readings and adjusts the amount of fuel injected to compensate for variations in engine conditions, component wear, or other factors. By understanding how to read fuel trims VCDS, you gain insights into the engine’s performance and can identify potential issues. These trims are expressed as percentages, indicating whether the ECU is adding or subtracting fuel.
Similar to vcds for vw, VCDS allows you to access this information in various Volkswagen group vehicles. Positive fuel trim values indicate the ECU is adding fuel, suggesting a lean condition (too much air relative to fuel). Negative values, conversely, mean the ECU is reducing fuel, pointing to a rich condition (too much fuel compared to air).
How to Access Fuel Trims Using VCDS
Accessing fuel trims with VCDS is straightforward. First, connect your VCDS interface to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and launch the software. Select the correct vehicle model and engine code. Navigate to the “Engine” module and then “Measuring Blocks.” Locate the measuring block groups that display fuel trims. These groups often vary depending on the specific engine and model, but they are usually labeled as “Fuel Trim Bank 1” and “Fuel Trim Bank 2” for engines with two cylinder banks.
What are the common fuel trim measuring block groups? Often, they’re labeled as “Fuel Trim Bank 1” and “Fuel Trim Bank 2” in VCDS for dual-bank engines.
Interpreting Fuel Trim Readings
Interpreting fuel trim readings requires understanding both short-term and long-term fuel trims. Short-term fuel trim (STFT) reflects immediate adjustments to the air-fuel ratio based on real-time oxygen sensor data. Long-term fuel trim (LTFT) represents learned corrections over time, compensating for consistent deviations. Ideally, STFT should fluctuate around zero, while LTFT should remain relatively stable within a narrow range.
How do STFT and LTFT interact? STFT makes immediate adjustments, while LTFT learns from these adjustments to compensate for consistent deviations.
Significant deviations from these ideal ranges can signal underlying problems. For instance, consistently high positive fuel trims may indicate vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, or low fuel pressure. Consistently negative fuel trims might suggest issues like a clogged air filter, malfunctioning fuel injectors, or a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
Troubleshooting Common Fuel Trim Issues with VCDS
VCDS provides a powerful tool for troubleshooting fuel trim issues. By analyzing the data, you can pinpoint the root cause of the problem. For example, if you observe high positive fuel trims, you can use VCDS to check for vacuum leaks by monitoring the intake air pressure or performing a smoke test. Similarly, if you suspect a faulty oxygen sensor, you can use VCDS to monitor its readings and compare them to expected values. Understanding fuel trim vcds allows you to effectively diagnose these issues.
How can VCDS help pinpoint fuel trim problems? It allows you to monitor various engine parameters, such as intake air pressure and oxygen sensor readings, to identify the root cause.
Advanced VCDS Techniques for Fuel Trim Analysis
Beyond basic fuel trim readings, VCDS offers advanced features for in-depth analysis. You can log fuel trim data over time to observe trends and identify intermittent issues. You can also compare fuel trims across different engine operating conditions, such as idle, partial throttle, and full throttle, to pinpoint specific problems. Accessing vcds wiki codes can provide further insights into specific error codes and their relation to fuel trims. Just as with what is vcds scan audi, understanding the intricacies of these systems is vital for accurate diagnosis.
What advanced features does VCDS offer for fuel trim analysis? Data logging, comparison across different operating conditions, and access to specific error codes provide a more comprehensive diagnostic approach.
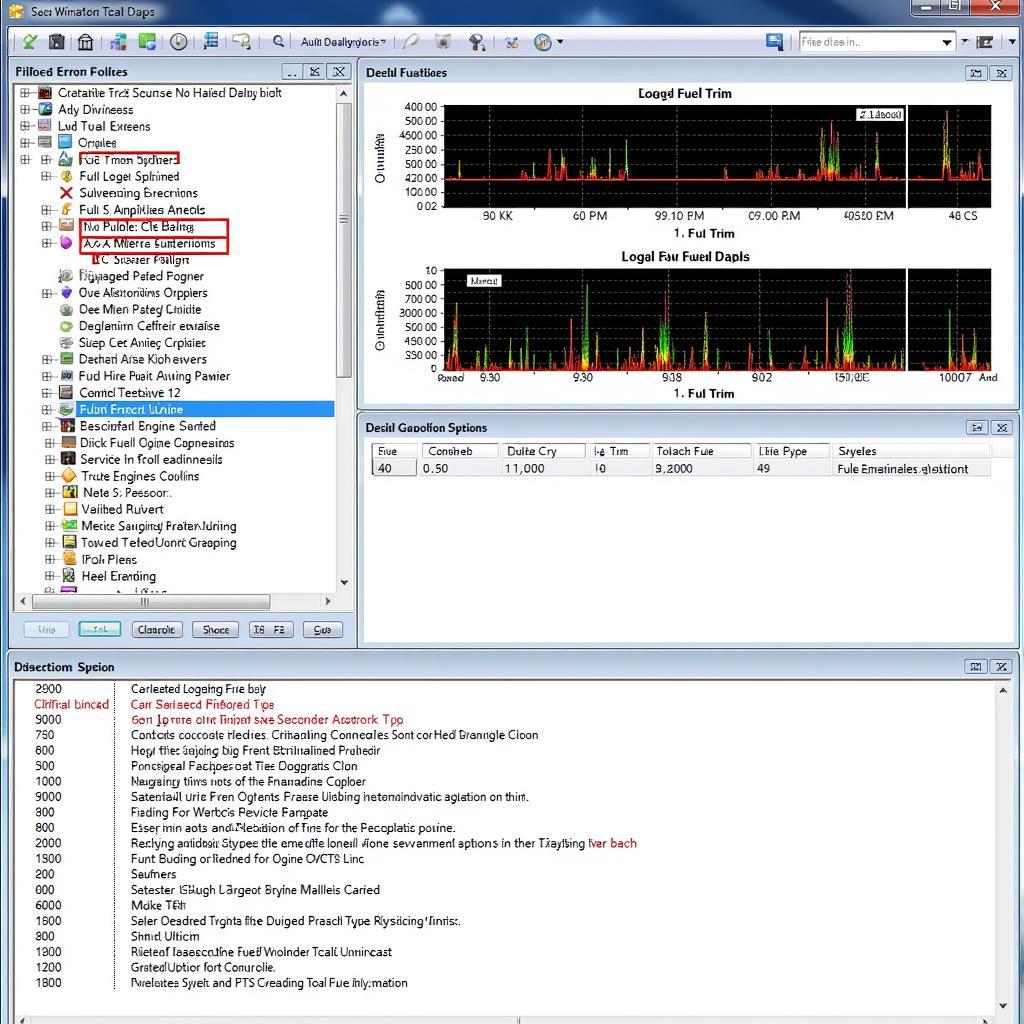 Advanced Fuel Trim Diagnostics with VCDS
Advanced Fuel Trim Diagnostics with VCDS
Conclusion
Mastering how to read fuel trims VCDS empowers you to effectively diagnose and address engine performance issues. By understanding the significance of STFT and LTFT, interpreting their readings, and utilizing VCDS’s advanced features, you can pinpoint problems and implement appropriate solutions, ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Knowing how to read fuel trims vcds is an essential skill for any automotive technician or enthusiast.
FAQ
- What are fuel trims?
- Why are fuel trims important?
- How do I access fuel trims using VCDS?
- What do positive and negative fuel trims indicate?
- How do I troubleshoot common fuel trim issues?
- What are short-term and long-term fuel trims?
- What are some advanced VCDS techniques for fuel trim analysis?
For further information, explore our resources on vcds cars.
Need help? Contact us via Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, Email: CARDIAGTECH[email protected] or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Our 24/7 customer support team is ready to assist you.