City safety and collision warning with full auto brake are both advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) designed to prevent or mitigate collisions. While they share a common goal, there are key differences that drivers should understand. This article dives deep into the functionalities of each system, comparing their features, limitations, and real-world applications to help you grasp the distinctions.
Understanding City Safety
City Safety is Volvo’s brand name for its low-speed collision avoidance system. It primarily focuses on mitigating or preventing collisions in urban environments, typically at speeds below 31 mph (50 km/h). City Safety uses a laser sensor mounted near the top of the windshield to constantly monitor the distance to vehicles in front. If a collision is imminent and the driver fails to react, City Safety automatically applies the brakes to avoid or lessen the impact.
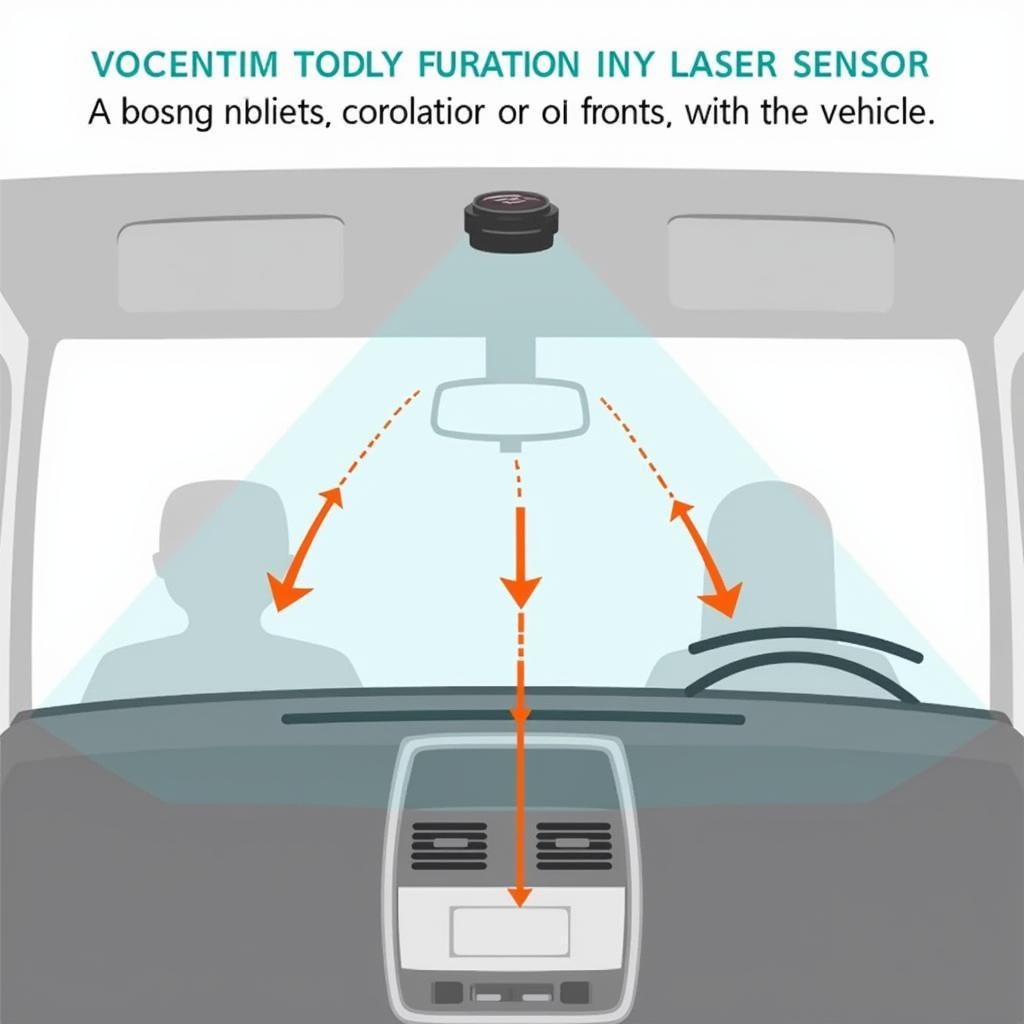 City Safety Laser Sensor
City Safety Laser Sensor
City Safety systems are often integrated with other safety features, such as pedestrian and cyclist detection. This broader functionality enhances protection in complex urban scenarios involving vulnerable road users. Depending on the specific Volvo model and year, City Safety may also include features like steering support to help avoid obstacles.
Exploring Collision Warning with Full Auto Brake
Collision warning with full auto brake is a more general term used by various car manufacturers to describe systems similar in function to City Safety but often with a broader operational speed range. These systems typically utilize radar, cameras, or a combination of both to detect potential collisions at higher speeds, extending beyond the urban focus of City Safety.
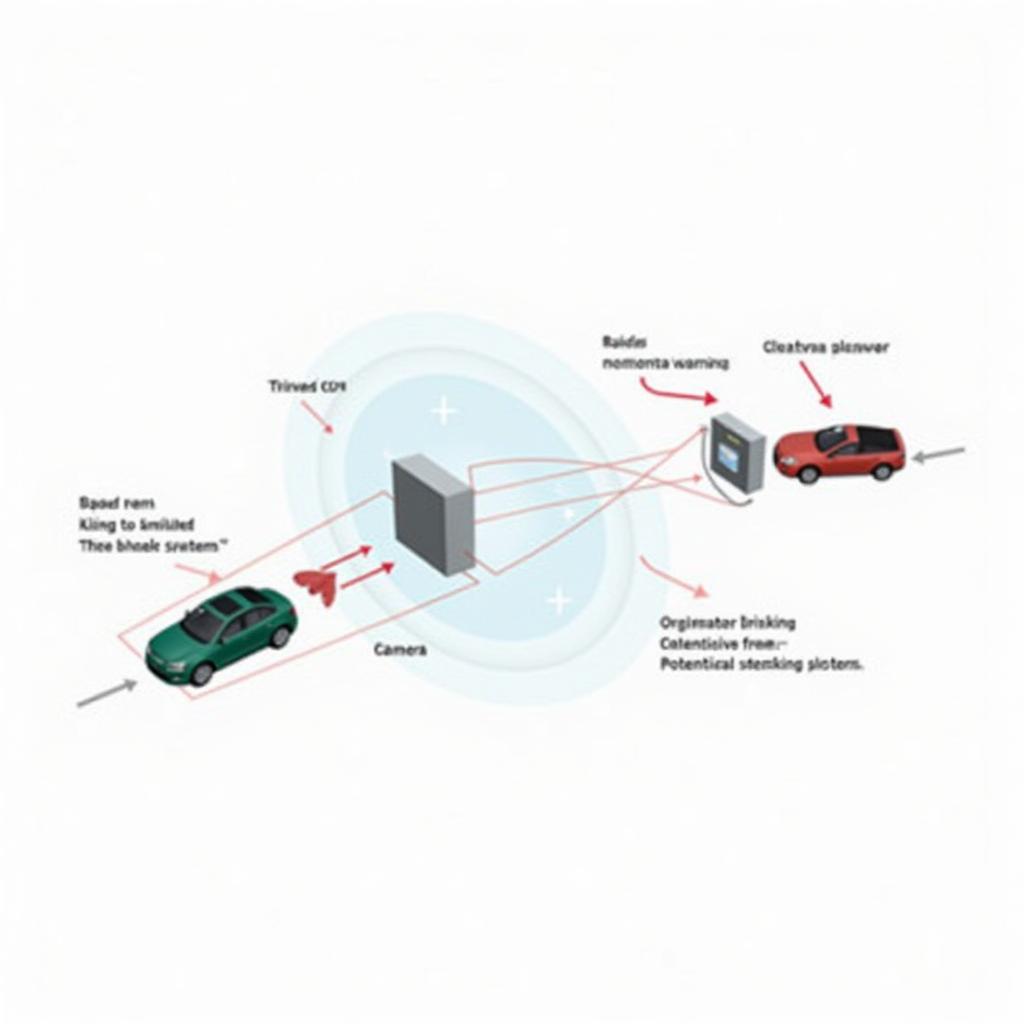 Collision Warning System Components
Collision Warning System Components
Unlike City Safety, which focuses primarily on automatic braking, collision warning systems often include an initial warning stage. This typically involves visual and audible alerts to prompt the driver to take action. If the driver fails to respond, the system then engages automatic emergency braking to mitigate the collision’s severity.
Key Differences: City Safety vs. Collision Warning
The primary difference between City Safety and collision warning with full auto brake lies in their specific implementation and branding. City Safety is a Volvo-specific term, whereas collision warning with full auto brake is a generic term. Furthermore, City Safety traditionally focuses on low-speed urban situations, while collision warning systems generally operate across a broader speed range.
“City Safety offers a robust low-speed collision mitigation solution, ideally suited for navigating congested urban areas,” says automotive safety expert, Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading researcher in ADAS technology. “While collision warning with full auto brake extends protection to higher speeds, drivers must remember that these systems are not foolproof and should not replace attentive driving.”
Driving with Confidence: Understanding ADAS Limitations
While ADAS features like City Safety and collision warning with full auto brake significantly enhance safety, it’s crucial to understand their limitations. These systems are designed as driver aids, not replacements for attentive driving. Factors like weather conditions, sensor limitations, and unexpected obstacles can impact their effectiveness.
“Drivers should always remain vigilant and prepared to take control,” adds Dr. Sharma. “ADAS features are valuable tools, but they should never be interpreted as an invitation for distracted or reckless driving.”
Conclusion: Enhancing Safety on the Road
Both City Safety and collision warning with full auto brake contribute significantly to enhancing road safety by helping drivers avoid or mitigate collisions. While City Safety is Volvo’s specialized solution for low-speed urban environments, collision warning systems provide a more generalized approach across a wider speed range. Understanding the nuances of each system empowers drivers to utilize these technologies effectively and safely. Remember, ADAS is a valuable asset, but attentive driving remains paramount.
FAQs
-
Does City Safety work at highway speeds? No, City Safety is primarily designed for low-speed urban driving, typically below 31 mph (50 km/h).
-
Can collision warning systems prevent all accidents? No, while they can significantly reduce the likelihood and severity of collisions, factors like weather, sensor limitations, and unexpected obstacles can affect their performance.
-
What is the difference between automatic emergency braking (AEB) and collision warning? Collision warning alerts the driver of a potential collision, while AEB automatically applies the brakes if the driver fails to react. Many systems combine both features.
-
Do all cars have collision warning systems? No, while becoming increasingly common, these systems are not standard on all vehicles.
-
How do I know if my car has City Safety or collision warning? Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or contact the manufacturer for specific information about your vehicle’s safety features.
-
Can I turn off City Safety or collision warning? Most systems allow drivers to temporarily disable the feature through the vehicle’s settings menu, but it’s generally recommended to keep them activated.
-
How often should I have my ADAS system checked? It’s recommended to have your ADAS system inspected and calibrated according to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule.

