Low battery voltage can cause a frustrating array of problems in your car. From dimming headlights to a complete engine stall, understanding these symptoms is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s health and preventing unexpected breakdowns. This guide will delve into the common low battery voltage symptoms, their causes, and how you can diagnose and address them.
Recognizing Low Battery Voltage Symptoms
Several telltale signs indicate your car might be suffering from low battery voltage. These symptoms can range from minor inconveniences to major malfunctions.
- Dim Headlights: One of the earliest and most noticeable signs is dimming headlights, especially when idling or at low RPMs.
- Slow Cranking: If your engine cranks slowly or struggles to turn over, it’s a strong indicator of low battery voltage.
- Electrical Malfunctions: Power windows operating slowly, a malfunctioning radio, or flickering interior lights can all point to a weakened battery.
- Dashboard Warning Lights: The check engine light, battery light, or other warning lights on your dashboard can illuminate due to low voltage.
- Clicking Sound When Starting: A rapid clicking sound when you turn the key often signifies the starter motor isn’t receiving enough power due to low battery voltage.
- Security System Issues: what is anti theft system that activates when key removed Sometimes, a low battery voltage can trigger the anti-theft system, preventing the car from starting.
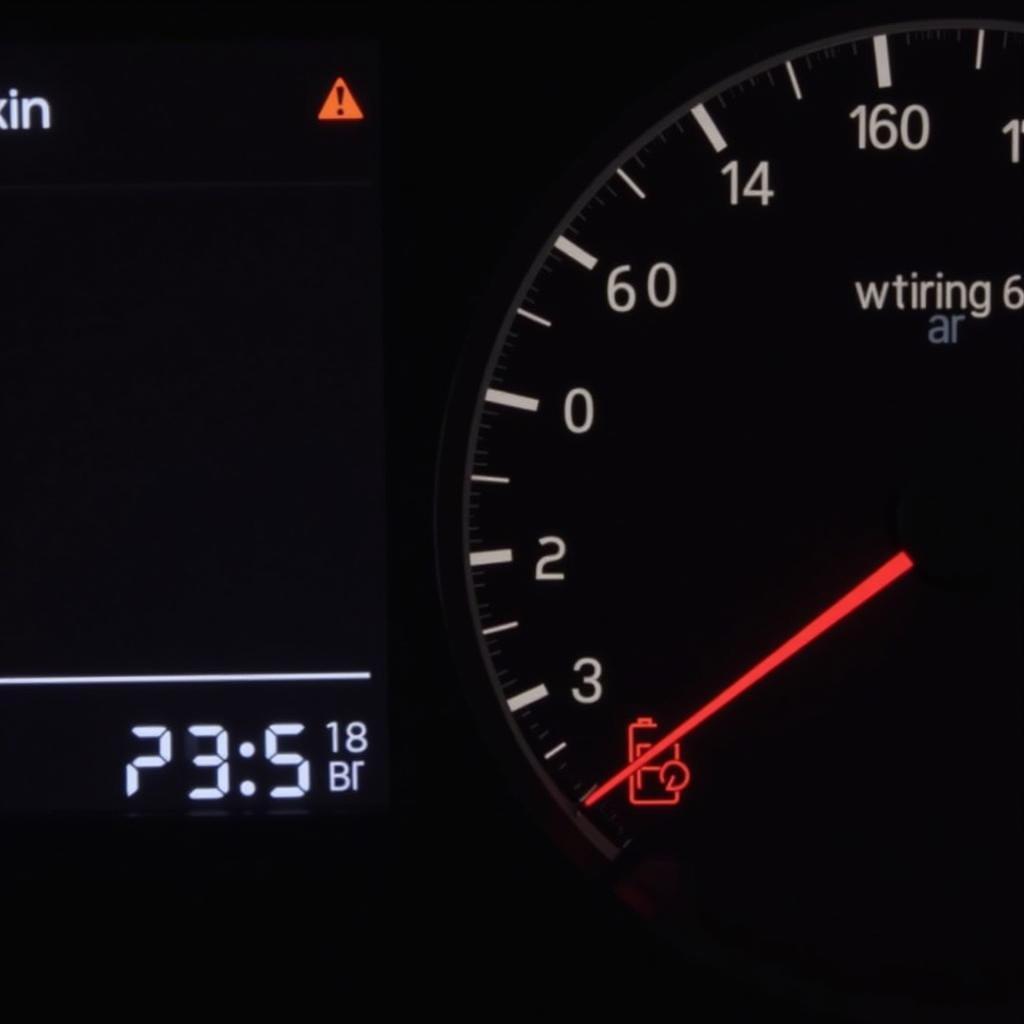 Dashboard Showing Low Battery Voltage Warning Light
Dashboard Showing Low Battery Voltage Warning Light
What Causes Low Battery Voltage?
Understanding the root causes of low battery voltage is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
- Old Battery: Batteries have a limited lifespan, typically 3-5 years. As they age, their ability to hold a charge diminishes.
- Parasitic Drain: Even when the car is off, certain electrical components can draw power, slowly draining the battery. This can be due to faulty wiring, malfunctioning modules, or even leaving interior lights on.
- Failing Alternator: The alternator recharges the battery while the engine is running. A faulty alternator won’t charge the battery effectively, leading to low voltage.
- Extreme Temperatures: Both extreme heat and cold can negatively impact battery performance.
- Corroded Battery Terminals: Corrosion on the battery terminals can hinder the flow of electricity, resulting in low voltage.
Diagnosing and Fixing Low Battery Voltage
Addressing low battery voltage often involves a systematic approach to identify and resolve the underlying issue.
- Visual Inspection: Check the battery terminals for corrosion. Clean them with a wire brush and baking soda solution if necessary.
- Battery Test: Use a multimeter or a battery tester to check the battery’s voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Alternator Test: With the engine running, the voltage should be around 14 volts. A lower reading suggests a problem with the alternator.
- Parasitic Drain Test: Use an ammeter to measure the current draw when the car is off. An excessive draw indicates a parasitic drain.
“Regular battery maintenance, including cleaning terminals and checking voltage, can significantly extend battery life and prevent unexpected starting problems,” advises John Smith, Lead Automotive Electrical Engineer at AutoTech Solutions.
How Can Remote Diagnostics Help?
Modern vehicles are equipped with sophisticated onboard diagnostic systems. Remote diagnostics and software programming can play a crucial role in identifying and addressing low battery voltage issues. By analyzing data from these systems, technicians can pinpoint the root cause, even remotely.
“Remote diagnostics allow us to quickly identify the source of the problem, whether it’s a faulty alternator, a parasitic drain, or simply an aging battery,” says Emily Johnson, Senior Diagnostic Technician at Remote Automotive Services. “This saves time and money for the customer, as we can often avoid unnecessary trips to the repair shop.”
Conclusion
Low battery voltage symptoms can manifest in various ways, affecting the performance and reliability of your vehicle. By recognizing these symptoms, understanding their causes, and taking proactive steps for diagnosis and repair, you can avoid frustrating breakdowns and ensure your car is always ready to go. Regular battery maintenance and utilizing remote diagnostics can significantly enhance your car’s longevity and prevent future low voltage problems. Don’t let a weak battery leave you stranded – take charge of your car’s electrical health today.
FAQ
- How often should I check my car battery’s voltage? It’s recommended to check your battery voltage every few months, especially during extreme weather conditions.
- Can a low battery voltage damage other car components? Yes, prolonged low voltage can strain the alternator and other electrical components.
- How long does a car battery last? Car batteries typically last 3-5 years, depending on usage and climate.
- How can I prevent battery drain when the car is off? Make sure all lights are off, and avoid leaving accessories plugged in.
- What should I do if my car won’t start due to a dead battery? Try jump-starting the car or call for roadside assistance.
- Can I replace a car battery myself? Yes, you can replace a car battery yourself with basic tools, but it’s essential to follow safety precautions.
- What is the cost of a new car battery? The cost varies depending on the type and size of the battery, but typically ranges from $50 to $200.


