The world of automotive diagnostics can feel like navigating a labyrinth. Among the numerous codes that might appear, the P2563 VCDS code often leaves car owners and even some mechanics scratching their heads. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the P2563 code, explaining its meaning, causes, symptoms, diagnostic steps, and potential solutions.
What Does the P2563 VCDS Code Mean?
Simply put, the P2563 code points to a problem with the “Turbocharger/Supercharger Boost Control Position Sensor ‘A’ Circuit.” Let’s break this down:
- Turbocharger/Supercharger: These components force more air into the engine, boosting power output.
- Boost Control Position Sensor: This sensor monitors the position of the turbocharger or supercharger boost control mechanism, providing critical data to the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
- “A” Circuit: This designation usually refers to a specific circuit, wire, or component within the boost control position sensor system.
In essence, the P2563 code signals that the ECU is receiving an implausible signal from the boost control position sensor’s “A” circuit. This inconsistency prevents the ECU from accurately managing boost pressure, potentially impacting engine performance and emissions.
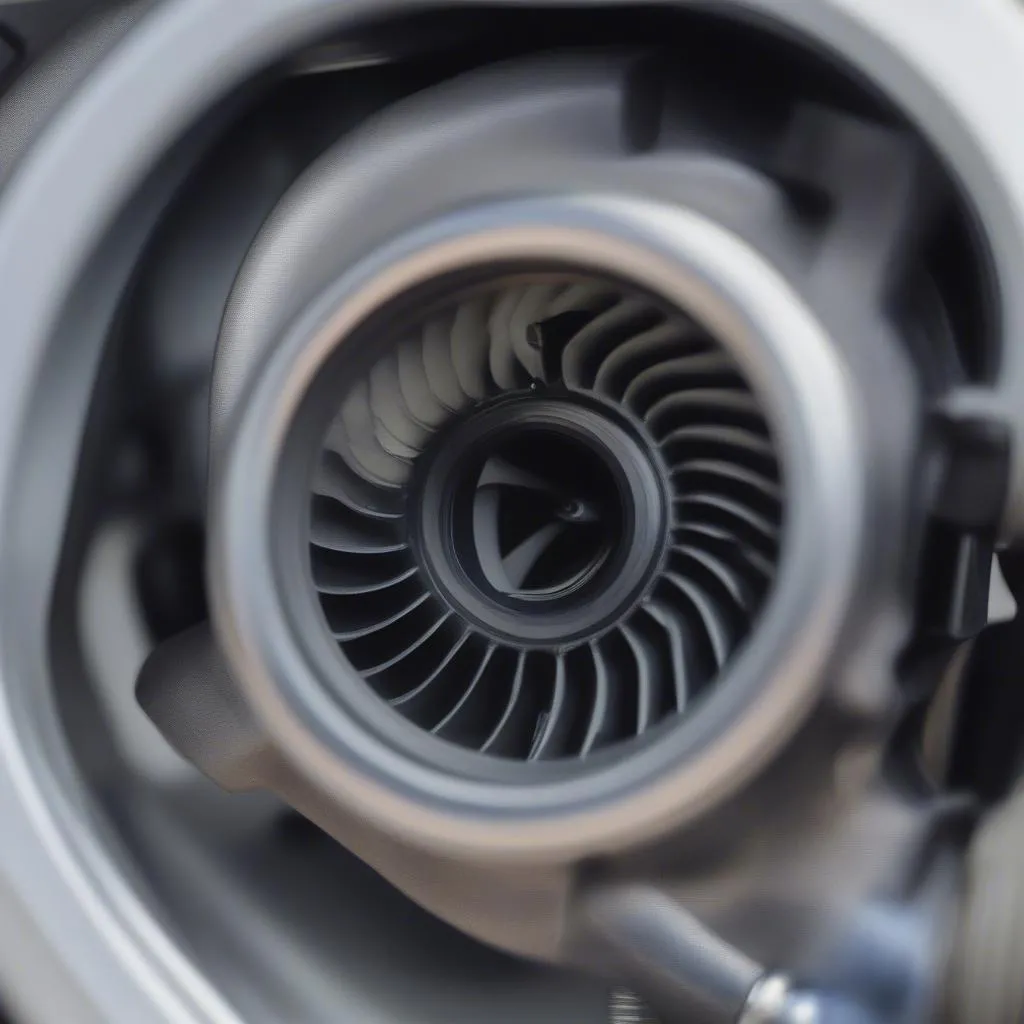 Turbocharger and Boost Control Position Sensor
Turbocharger and Boost Control Position Sensor
Causes of the P2563 Code
The P2563 code can be triggered by a range of issues, including:
- Faulty Boost Control Position Sensor: Over time, the sensor itself can wear out, become contaminated, or fail, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring within the sensor circuit can disrupt the signal to the ECU.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the vacuum lines controlling the boost mechanism can disrupt pressure readings and trigger the code.
- Turbocharger/Supercharger Issues: Problems within the turbocharger or supercharger itself, such as a sticking actuator or wastegate, can impact boost control and lead to the P2563 code.
- Faulty ECU: While less common, a malfunctioning ECU can misinterpret sensor data, resulting in erroneous fault codes.
 Car Engine Bay Wiring
Car Engine Bay Wiring
Symptoms of a P2563 Code
When the P2563 code is triggered, you may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Check Engine Light: This is often the first and most obvious sign of a problem.
- Reduced Engine Power (Limp Mode): To prevent engine damage, the ECU may limit engine output, resulting in sluggish acceleration and reduced power.
- Abnormal Engine Noises: Whistling or hissing sounds from the engine bay could indicate a boost leak.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Inefficient combustion due to incorrect boost pressure can lead to a drop in fuel economy.
 Check Engine Light on Car Dashboard
Check Engine Light on Car Dashboard
Diagnosing the P2563 VCDS Code
Accurate diagnosis is crucial before attempting any repairs. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Read the Codes: Use a reliable OBD-II scanner, such as those offered by CARDIAGTECH, to retrieve all stored fault codes, including any history codes.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the boost control position sensor, wiring harness, vacuum lines, and turbocharger/supercharger for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Sensor Testing: Using a multimeter, check the sensor’s resistance and voltage readings against manufacturer specifications.
- Wiring Check: Inspect the wiring harness for continuity and resistance, ensuring there are no breaks or shorts.
- Vacuum System Test: Check for leaks in the vacuum lines using a hand-held vacuum pump or by spraying soapy water around connections.
- Turbocharger/Supercharger Inspection: Inspect the turbocharger or supercharger for any signs of damage, play, or binding.