Experiencing problems with your 2002 Ford Explorer’s anti-theft system? A malfunctioning anti-theft system can be a real headache, leading to issues like starting problems or even a vehicle that won’t start at all. One common culprit behind these issues is a blown fuse. But how do you pinpoint which fuse is the troublemaker? This article will guide you through identifying and potentially replacing the fuse controlling your 2002 Ford Explorer’s anti-theft system.
Understanding the Problem
Before we delve into the solution, let’s understand why fuses blow. Fuses act as safety devices within your vehicle’s electrical system. When an electrical circuit experiences a surge or overload, the fuse sacrifices itself by blowing, effectively breaking the circuit and preventing damage to expensive components. In the case of an anti-theft system, a blown fuse can disrupt the communication between the key, immobilizer, and engine control unit, making it impossible to start your car.
Identifying the Culprit
Locating the exact fuse related to your 2002 Ford Explorer’s anti-theft system can be a bit tricky as fuse box layouts and fuse designations may vary. To identify the right one, you’ll need your owner’s manual.
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual is your best friend. It typically contains a fuse box diagram with a clear label indicating the anti-theft fuse.
- Check the Fuse Box Cover: Often, the fuse box cover itself will have a diagram.
Once you’ve identified the correct fuse, inspect it for signs of damage. A blown fuse is usually visually identifiable with a broken wire or a darkened glass section.
 Blown Car Fuse
Blown Car Fuse
What You’ll Need
Before you begin, gather these tools:
- Replacement Fuse: Make sure to use the correct amperage fuse as specified in your owner’s manual. Using the wrong amperage can be dangerous.
- Fuse Puller: This handy tool, often found inside the fuse box, makes removing and replacing fuses much easier.
Replacing the Fuse
- Safety First: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components.
- Locate the Fuse: Using the diagram, locate the anti-theft fuse in your fuse box.
- Remove the Fuse: Gently use the fuse puller to remove the fuse.
- Inspect the Fuse: Carefully examine the fuse for any signs of damage.
- Replace if Necessary: If the fuse is blown, insert the new fuse with the correct amperage.
- Reconnect Battery: Reattach the negative battery cable.
- Test the System: Try starting your vehicle to see if the issue is resolved.
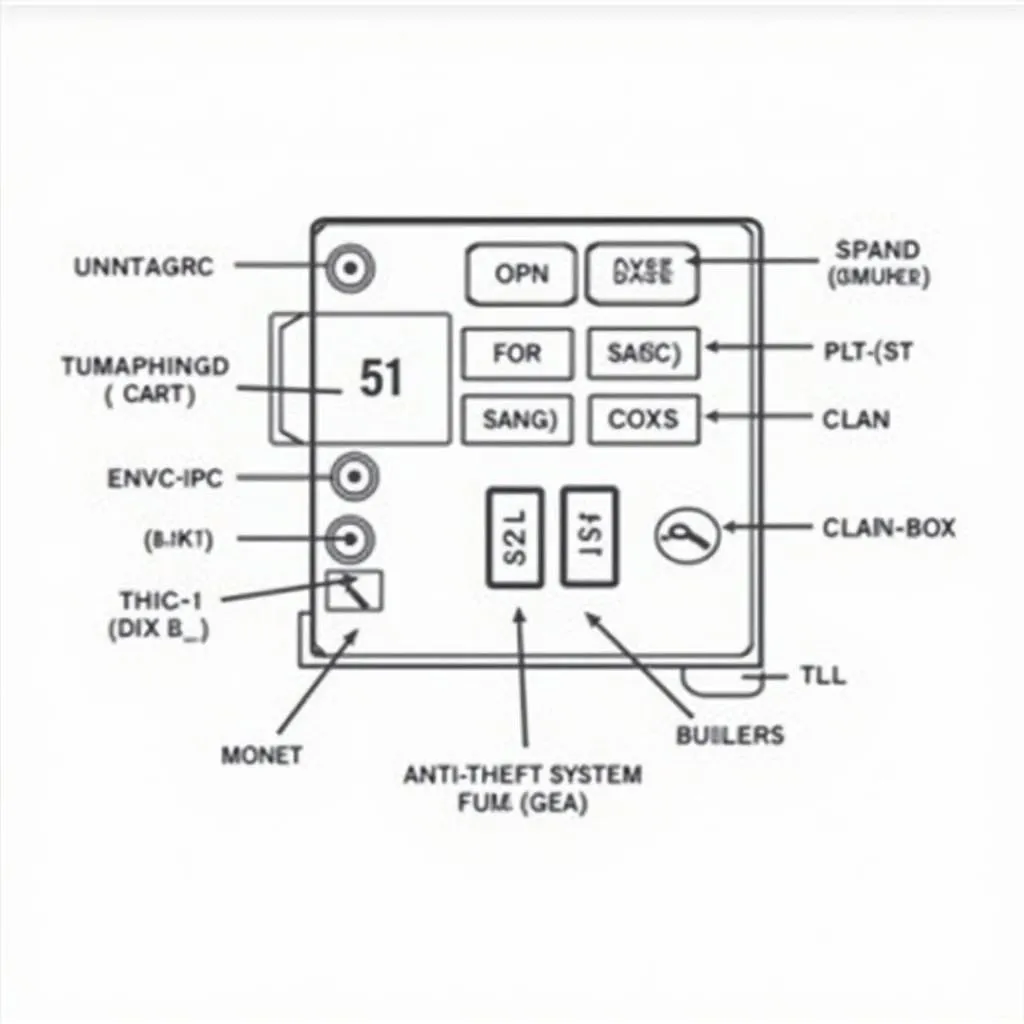 Car Fuse Box Diagram
Car Fuse Box Diagram
FAQs
Q: What if replacing the fuse doesn’t work?
A: If replacing the fuse doesn’t solve the problem, you’re likely facing a more complex issue within the anti-theft system itself. It’s time to seek the assistance of a qualified automotive electrician or take your vehicle to a trusted mechanic specializing in automotive electrical systems.
Q: Can I use any software to diagnose my car’s anti-theft system?
A: While several diagnostic tools are available, it’s crucial to choose a reputable and reliable option. Cardiagtech offers a range of high-quality diagnostic products specifically designed for automotive applications, ensuring accurate and efficient troubleshooting.
Conclusion
A blown fuse can be a frustrating but often easily resolvable issue with your 2002 Ford Explorer’s anti-theft system. By following these steps, you can confidently identify and potentially replace the fuse, getting you back on the road quickly. However, remember that electrical systems can be complex. If in doubt, don’t hesitate to contact a professional for assistance.
For more information and to explore our range of diagnostic solutions, visit Cardiagtech today.

