“Anti-theft” is a broad term that refers to any system in your car designed to deter thieves. While the specific features can vary widely between makes and models, their primary goal is to make stealing your vehicle much more difficult.
Understanding Your Car’s Security
Imagine your car’s anti-theft system as a series of safeguards working together. At the most basic level, you have:
1. Immobilizers: These systems, standard in most modern cars, prevent the engine from starting without the correct key. This technology uses a transponder chip embedded in your car key that communicates with the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU). Without the right signal from the key, the ECU won’t allow the engine to fire up.
2. Alarms: Car alarms act as deterrents. They typically use sensors to detect unauthorized entry, vibrations, or movement. Once triggered, the alarm system will sound a loud siren and may even flash the car’s lights, drawing attention to the attempted theft.
3. Tracking Systems: These systems utilize GPS or cellular technology to pinpoint your car’s location in case of theft. They can be invaluable in helping law enforcement recover your vehicle quickly.
4. Advanced Features: Some vehicles offer even more sophisticated anti-theft measures. These might include biometric authentication, remote kill switches, or even facial recognition systems.
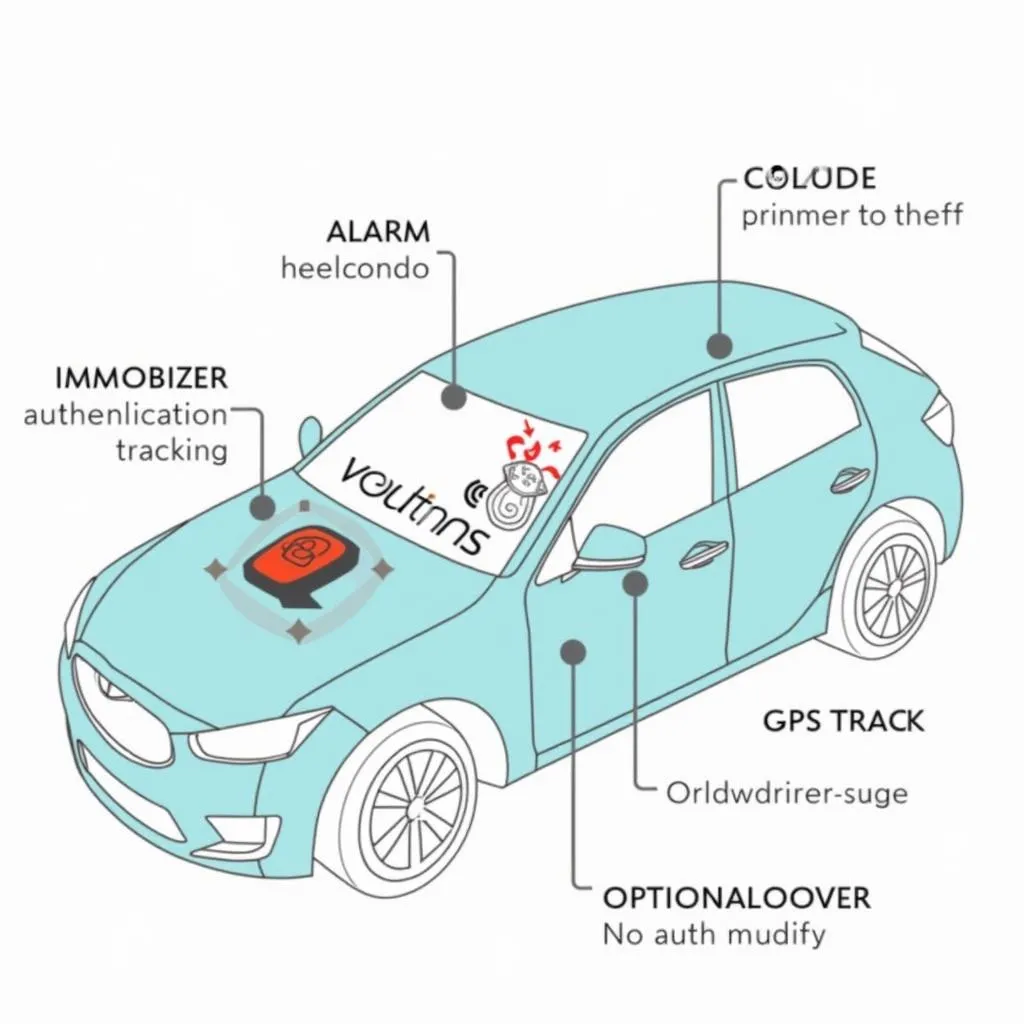 Car Anti-theft System Diagram
Car Anti-theft System Diagram
Identifying Anti-Theft System Issues
A malfunctioning anti-theft system can be quite frustrating, often resulting in a car that refuses to start or an alarm that won’t stop blaring. Common signs of a problem include:
- Flashing Security Light: A constantly flashing or illuminated security light on your dashboard is often the first indication of an issue.
- Engine Cranking but Not Starting: If your engine cranks but doesn’t turn over, the immobilizer system might not be recognizing your key.
- Frequent False Alarms: If your car alarm goes off without any apparent reason, it could be a sign of a faulty sensor or a wiring problem.
Troubleshooting Tools
Before attempting any DIY repairs, it’s important to have the right tools at hand:
- OBD-II Scanner: This handy device allows you to read diagnostic trouble codes from your car’s computer, helping you identify the root cause of the problem.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is essential for testing electrical circuits and components, such as fuses, relays, and sensors.
- Basic Hand Tools: A set of screwdrivers, pliers, and wrenches will come in handy for accessing and working on various components.
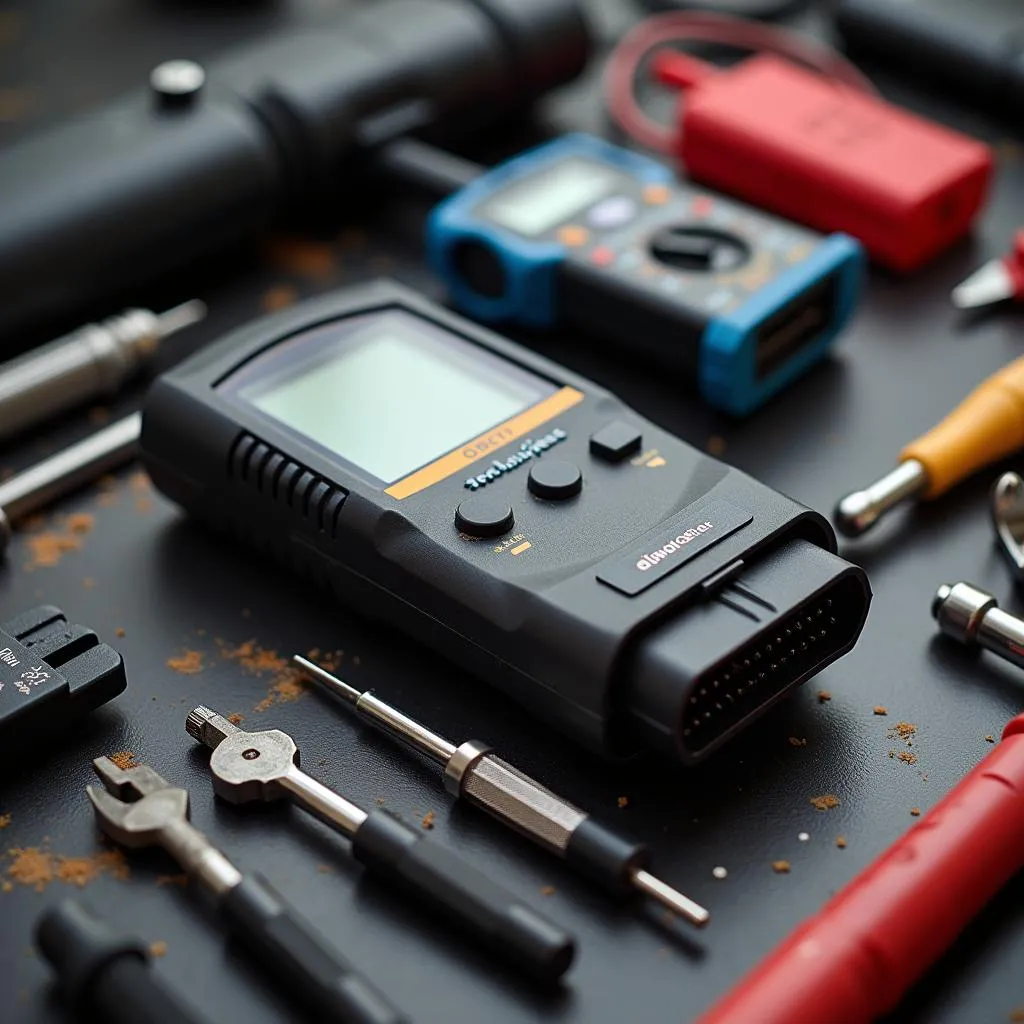 Essential Car Diagnostic Tools
Essential Car Diagnostic Tools
Repairing Anti-Theft System Issues
While simple issues like a dead key fob battery can be easily addressed, more complex problems often require professional expertise. “Attempting repairs without proper knowledge can sometimes worsen the problem,” says automotive electronics specialist Dr. Emily Carter, author of “Modern Automotive Security Systems.” “Consulting a qualified technician specializing in automotive electronics is always recommended.” They can accurately diagnose the issue and provide the correct solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I tell if my car has an anti-theft system?
A: Most modern cars come equipped with some form of anti-theft system. Check your owner’s manual or look for visual indicators like a flashing security light on the dashboard. You can also learn more about your car’s specific security features on websites like Cardiagtech.com.
Q: Can I install an aftermarket anti-theft system?
A: Yes, numerous aftermarket anti-theft devices offer additional layers of security. Consult with a reputable car audio or security shop for installation and compatibility advice.
Q: My car key is lost. What are my options?
A: Contact your dealership or a qualified locksmith specializing in automotive keys. They can help you order a replacement key and program it to your vehicle.
For further assistance with diagnosing and resolving anti-theft system issues, explore the range of diagnostic tools and resources available at CARDIAGTECH.com.

