Anti-theft transfer, in the context of modern vehicles, refers to the security measures designed to prevent unauthorized access and operation of a vehicle. These systems typically involve electronic components that communicate with various modules within the car, such as the engine control unit (ECU), the body control module (BCM), and the immobilizer system. Understanding anti-theft transfer is crucial for diagnosing and resolving vehicle starting issues, especially if you’re struggling with a car that won’t start even with a new battery. If you’ve recently installed a new battery but are still experiencing problems, check out our guide on new battery but car keeps dying.
How Does Anti-Theft Transfer Work?
Anti-theft transfer systems primarily rely on a coded key or key fob. When you insert the key or bring the fob near the vehicle, a signal is transmitted to the immobilizer system. This signal contains a unique code that the immobilizer verifies against its stored data. If the code matches, the immobilizer allows the engine to start. However, if the code is incorrect or if there’s a malfunction in the anti-theft system, the engine will be prevented from starting. Sometimes, even common car battery issues can mimic anti-theft problems, so it’s important to rule out those first. Learn more about common battery problems in our article about common car battery issues.
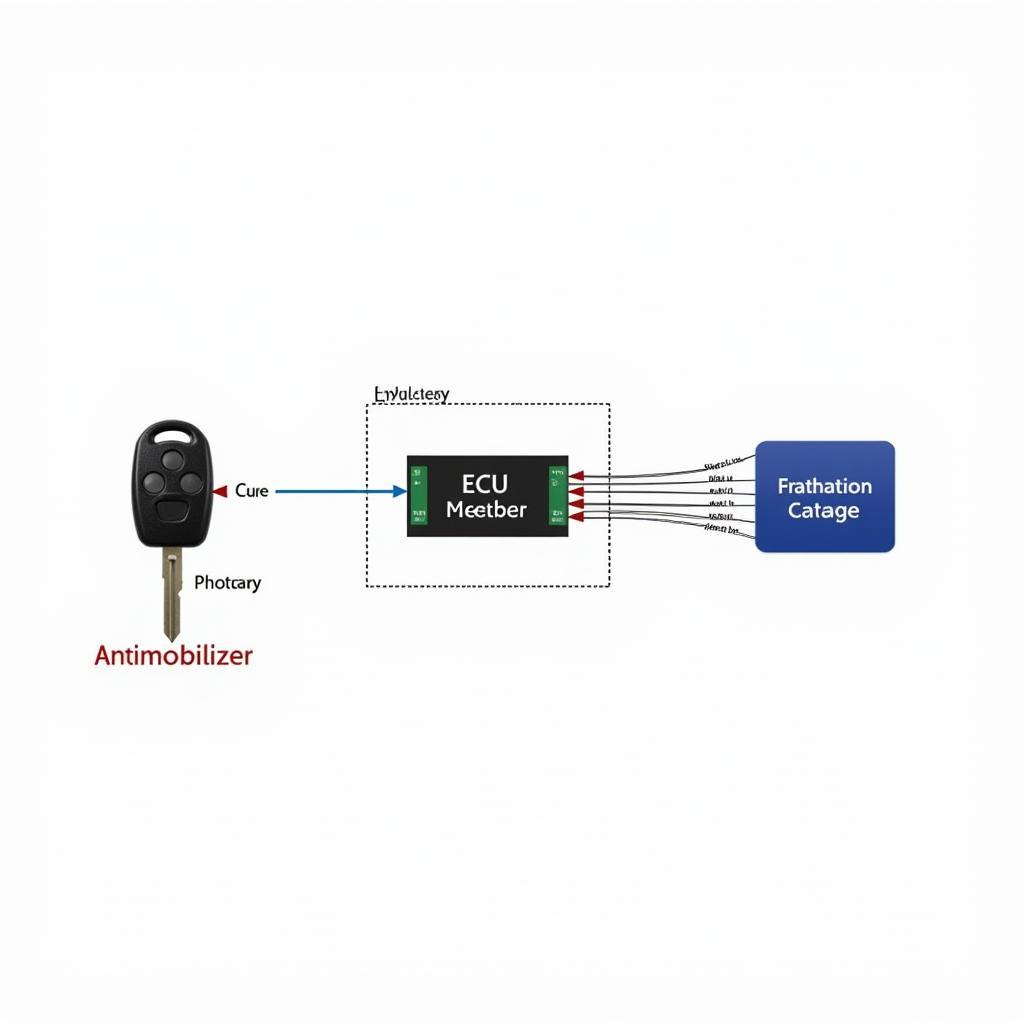 Anti-theft System Diagram
Anti-theft System Diagram
Common Issues with Anti-Theft Transfer Systems
Several issues can arise with anti-theft transfer systems, ranging from simple key fob battery failures to more complex electronic malfunctions. A weak key fob battery can disrupt the communication between the key and the immobilizer, preventing the engine from starting. Faulty wiring or connections within the anti-theft system can also cause problems. Moreover, damage to the immobilizer itself or the ECU can lead to anti-theft related starting issues. In some cases, a dying battery can trigger anti-theft systems, making it seem like the anti-theft system is the problem. You can learn how to check draw on car battery to rule out this possibility.
What are the signs of a malfunctioning anti-theft system?
Some common signs include the engine not starting, a flashing security light on the dashboard, and the inability to unlock the car doors with the key fob. If your car won’t start even though the battery isn’t dead, the anti-theft system could be the culprit. Refer to our guide on car wont start but battery isnt dead for more information.
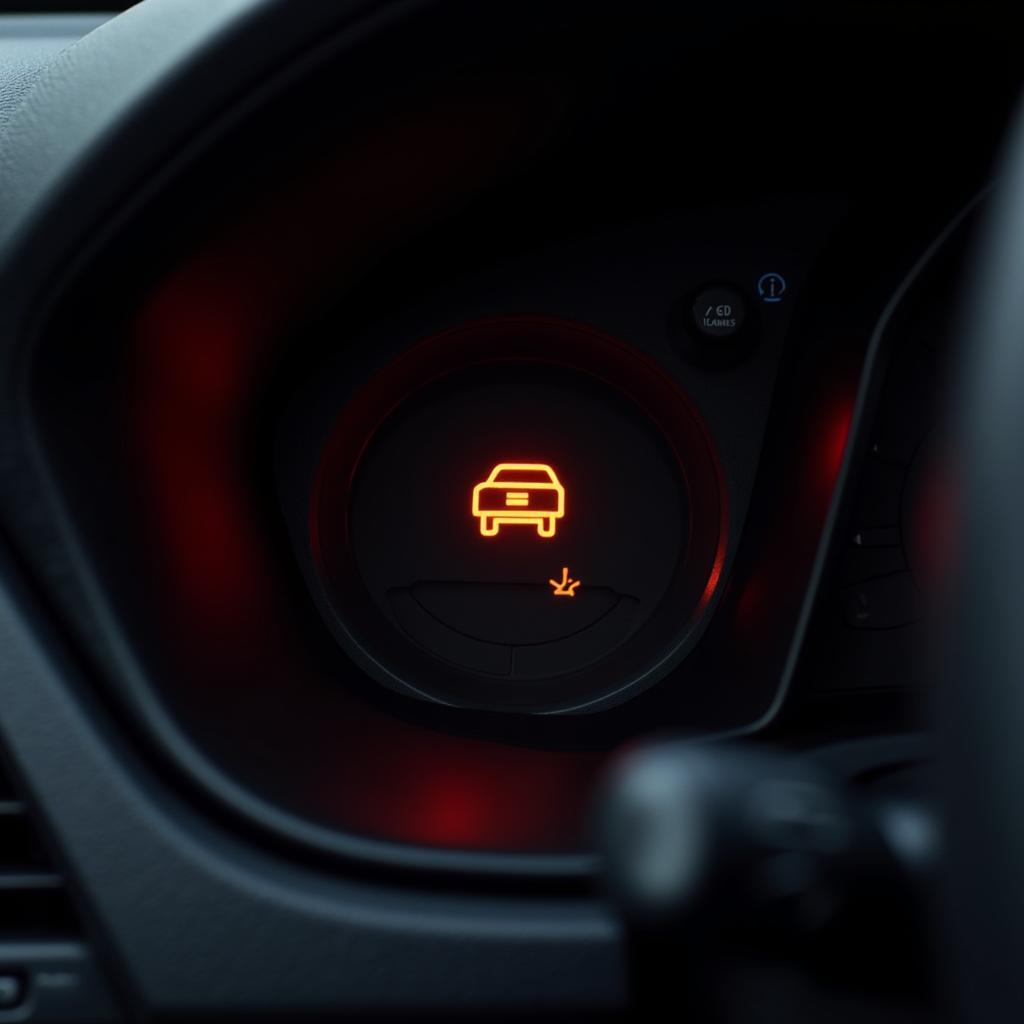 Car Dashboard Security Light
Car Dashboard Security Light
How to troubleshoot anti-theft transfer problems?
Start by checking the key fob battery. If replacing the battery doesn’t solve the issue, try using the spare key. If the spare key works, the issue likely lies with the original key fob. If both keys fail, the problem might be more serious, requiring professional diagnostics. Sometimes, temperature can affect battery performance, and a cold battery can struggle to start the car. This can sometimes be mistaken for an anti-theft problem. Read our article about car battery not starting in cold for tips on dealing with this.
Bypassing Anti-Theft Systems
Warning: Bypassing anti-theft systems should only be done by qualified professionals or in emergency situations. Attempting to bypass these systems without proper knowledge can damage the vehicle’s electronics.
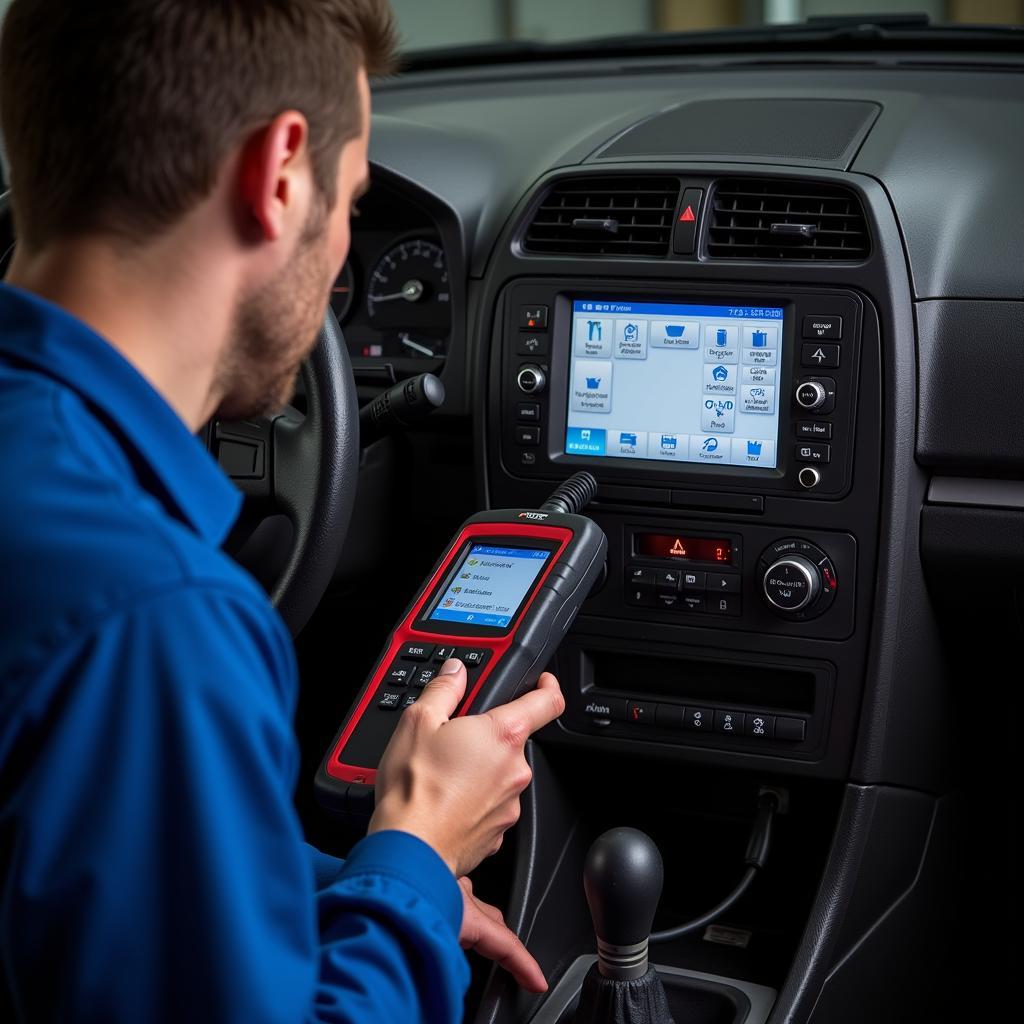 Car Diagnostic Tool
Car Diagnostic Tool
“Anti-theft systems are crucial for vehicle security. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any warning signs can prevent costly repairs and ensure the safety of your vehicle,” says John Thompson, Senior Automotive Technician at Acme Auto Repair.
“Modern vehicles heavily rely on complex electronic systems. Understanding how these systems interact is essential for effective diagnostics,” adds Maria Sanchez, Electrical Systems Engineer at Global Auto Solutions.
Conclusion
Anti-theft transfer is a vital component of modern vehicle security. Understanding how it works and being aware of potential problems can save you time, money, and frustration. If you’re experiencing issues with your car’s anti-theft system, consider seeking professional help for accurate diagnosis and repair. Addressing anti-theft transfer issues promptly ensures the security and reliable operation of your vehicle.
FAQ
- What is the purpose of an anti-theft transfer system? To prevent unauthorized vehicle operation.
- What are the common components of an anti-theft system? Key/key fob, immobilizer, ECU, and BCM.
- How can I tell if my anti-theft system is malfunctioning? Engine won’t start, flashing security light, key fob not working.
- What should I do if my key fob battery is dead? Replace it with a new battery.
- Can I bypass the anti-theft system myself? It’s not recommended unless you’re a qualified professional.
- What is the most common cause of anti-theft system problems? Key fob battery failure or faulty wiring.
- How can I prevent anti-theft system issues? Regular maintenance and attention to warning signs.


